TID Recommendations for Organ Donation and Transplantation after COVID-19 - October 2022
Lead author: Stephanie Pouch
Co-authors: Wanessa Trrindade Clemente, Marcelo Radisic
Review and editing: Ban Hock Tan
Council’s note: In this update, we focus primarily on the question of donors and recipients who are having or have recently had COVID-19. The previous updates are considered archived.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on donor evaluation and organ procurement.1 As the virus entrenches itself, the risk of donor-derived infection must be balanced with the risk of morbidity and mortality while remaining on the transplant waitlist. Decisions to proceed with organ transplant locally must balance the existing capacity of the center, availability of testing for donors and candidates, and sufficient capacity to provide adequate occupational protection to recovery and transplant staff.2
The recommendations in this document are based upon current peer-reviewed literature and public health data and represent a consensus opinion from TID Council, all of whom are practicing clinicians. Given that knowledge about SARS-CoV-2 continues to evolve, the recommendations contained in this document are subject to change. Additionally, the authors recognize that access to diagnostic assays may vary globally, particularly in resource-limited settings, and local approaches to donor evaluation may need to be adopted accordingly.
- Nucleic acid tests (NAT) are the preferred screening tests for COVID-19 in both potential donors and potential recipients.
- Organs other than lungs and intestines may be retrieved for transplant from SARS-CoV-2-positive deceased donors for transplant. Different countries are in varying stages of opening up, and there will be different levels of acceptance of such organs among patients. An informed consent process is essential. Infection prevention considerations vary by centre – these have to be factored into the decision to proceed with the transplant in such cases.
- There is no data to support pre-emptive anti-virals or monoclonals in persons who have just received an organ from a donor who is COVID-19 positive.
- We recommend that living donors be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 prior to donation.
- Living donation may proceed in a potential donor who is beyond 4 weeks of recovery from COVID-19, provided a pre-anesthesia assessment is conducted.
- All potential recipients should undergo COVID-19 screening.
- Potential recipients who have recovered from COVID-19 may undergo a transplant if they had mild COVID-19, if there has been an interval of ≥ 14 days after symptom onset (or initial positive test). Patients who had severe COVID-19 may undergo a transplant if ≥ 28 days have elapsed after symptom onset (or initial positive test).
- In patients who need a transplant urgently, careful and thorough discussion among the transplant and ICU teams, patient (if communicative) and family members is advised. Depending on the usual protocols in the hospital, the input of the hospital’s ethics committee may be invoked.
- In circumstances where the PCR remains positive despite apparent clinical recovery from COVID-19, the trend in Ct values may assist in the decision to proceed with transplant. Ct values, however, are dependent on many variables (eg, source of sample, platform, etc) and must be interpreted with cautious circumspection, with meticulous attention to detail.
| Term or Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|
| Asymptomatic COVID-19 infection | Detection of SARS-CoV-2 on an antigen or nucleic acid test without current or previous symptoms |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| Ct | Cycle threshold |
| Date of disease onset | Date of onset of COVID-19 symptoms OR date of SARS-CoV-2 test positivity |
| Fully vaccinated | Completion of the primary vaccine series plus a booster |
| LRT | Lower respiratory tract sample |
| NAT | Nucleic acid test |
| NP | Nasopharynx |
| OP | Oropharynx |
| POC | Point of care |
| RAT | Rapid antigen test |
| Resolved COVID-19 | History of confirmed COVID19 at least 21 days prior and with resolution of symptoms |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RT-PCR | Real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| URT | Upper respiratory tract sample |
SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic assays are based on the detection target. There are 3 types of diagnostic tools: 1) nucleic acid tests (NAT), which detect the presence of viral ribonucleic acid (RNA), typically by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or transcription-mediated amplification (TMA); 2) Rapid antigen tests (RAT), which detect the presence of a viral antigen, generally nucleocapsid; and 3) antibody tests that identify antibodies generated against SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) or nucleocapsid (N) antigens, both binding and neutralizing.
NAT is considered the gold standard for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection. NAT may detect one or more viral RNA genes and a positive result indicates current or recent infection. However, prolonged viral RNA detection is not always indicative of replication-competent virus. NAT samples are typically obtained from the upper respiratory tract (URT), including the nasopharynx (NP) or throat/oropharynx (OP), or lower respiratory tract (LRT), including sputum, tracheal aspirate, bronchial washing, or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. Combining NP with OP swabs might improve sensitivity. Point-of-care (POC) molecular tests have a rapid turn-around time but sensitivity varies by test.
Cycle threshold (Ct) values may be obtained from some NAT platforms and indicate the number of amplification cycles at which fluorescence of the PCR product is detectable over and above the background signal. Several studies have attempted to address the correlation between SARS-CoV-2 RNA load and infectiousness. Generally, low Ct values correlate with a higher viral load, and high Ct values correlate with lower viral loads.3 However, Ct values from different assays in different laboratories are not directly comparable, and multiple factors, including mechanism and quality of sample collection, timing of sampling with respect to infection or onset of symptoms, and duration of shedding, can all affect results. Therefore, caution is advised when interpreting Ct values. While sequential Ct values can give an indication of trend, assessment of sequential values should only be used in the full context of epidemiological, clinical and other laboratory information.
RATs have similar specificity but are less sensitive than most NATs. Antibody tests are used for public health surveillance and epidemiologic purposes. Notably, different assays identify binding and/or neutralizing antibodies; some have shown a good correlation of antibody titration results with virus-neutralizing antibodies. Assays can measure antibodies against the viral S or N proteins; anti-S positivity can be seen following natural infection or vaccination. Antibody testing is not recommended to either diagnose current infection or for donor/recipient screening purposes.
The SARS-CoV2 OMICRON variant, with the exception of the BA2 sub-lineage, yields, with some PCR assays, a reading called the S-gene dropout. This is due to a deletion in the code related to the spike protein, causing failure to amplify the S target in some assays (S-gene target failure). Overall accuracy should not be affected in tests that use multiple genetic targets. This was seen with the Delta variant and highlights the importance of monitoring test performance against evolving virus variants.
Screening should begin with a review of donor history, including recent exposure to persons with known or suspected COVID-19; personal history of COVID-19, including timing of symptom onset and date(s) of previous testing if available; COVID-19 vaccination history, and any symptom consistent with COVID-19 at the time of terminal hospitalization.
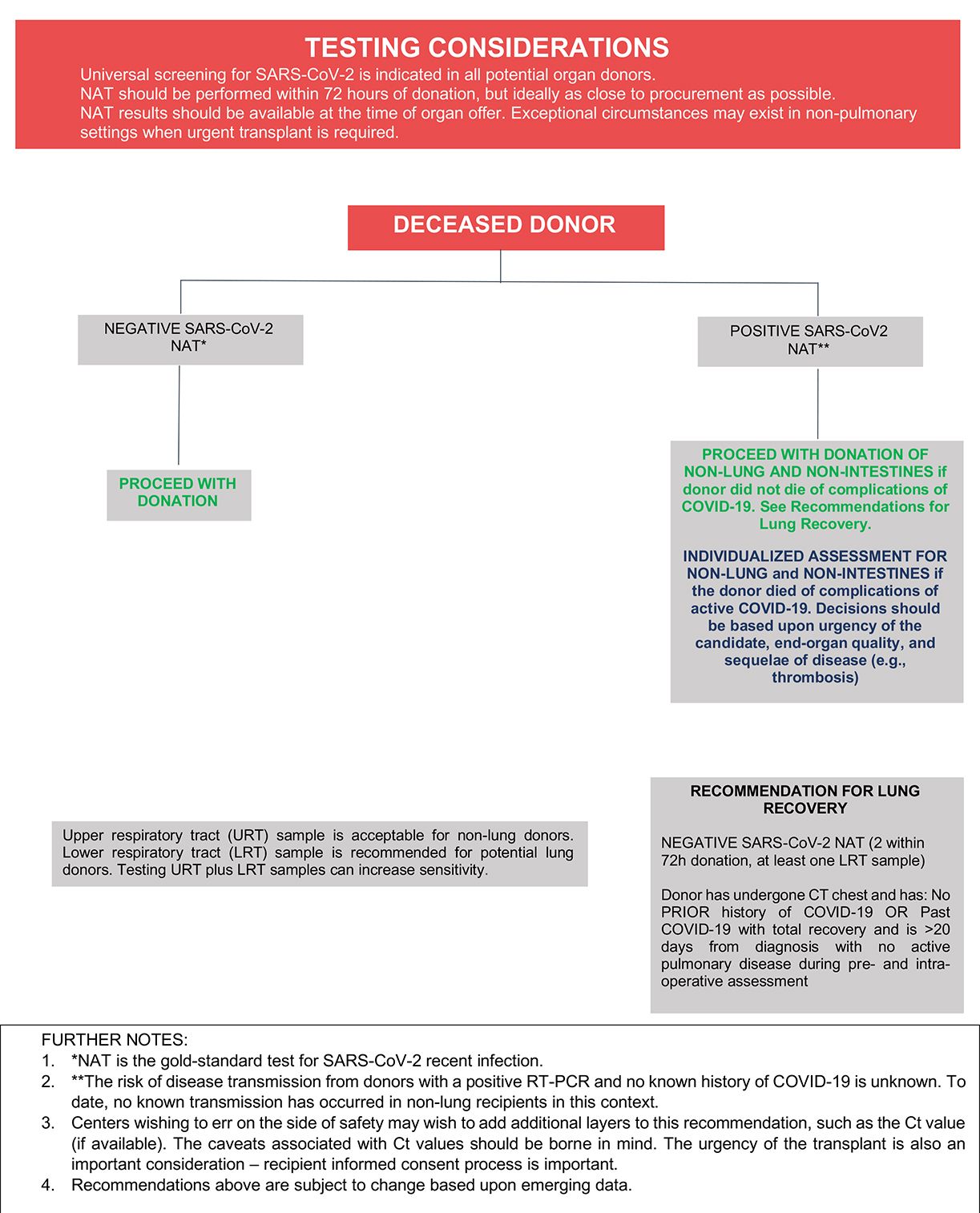
The recommended laboratory assessment of deceased donors for SARS-CoV-2 infection is outlined in Figure 1. All transplant societies strongly recommend universal screening by NAT of potential organ donors before procurement (Table 1), and sampling of upper and lower respiratory tract can increase sensitivity among deceased donors. Yield is better from lower respiratory tract specimens, especially in patients with abnormal chest imaging. Sequential NAT could improve overall sensitivity and test performance where required. Potential lung donors should undergo LRT NAT.4
Donor SARS-CoV-2 testing using serology or antigen detection is not recommended.5 Routine imaging may provide help in risk stratifying donors, although lung abnormalities are common in donors without COVID-19 and should not be used in isolation in the diagnosis of COVID-19.6
In general, the framework outlined in Figure 1 may be used to inform decisions about whether to proceed with recovery and transplantation of organs from deceased donors with a history of COVID-19 and/or who are found to have a positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT at the time of terminal hospitalization or donor evaluation. To date, there have been three cases of SARS-CoV-2 transmission to lung transplant recipients from donors with initial negative URT NAT testing but who retrospectively tested positive by NAT from LRT samples.4 At present, there have been no known transmissions to non-lung recipients of organs recovered from donors with positive URT or LRT SARS-CoV-2 NAT results,4 and, there is increasing experience with the transplantation of non-lung organs from donors with positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT results at the time of organ recovery without a clear signal for adverse short-term allograft outcomes.7-21 Furthermore, recently published larger-scale experience from the United States has shown that recipients of non-lung organs from SARS-CoV-2 NAT-positive donors have short-term patient and graft survival similar to those who received organs from SARS-CoV-2 NAT-negative donors.22-24 These published experiences are encouraging, and organs from SARS-CoV-2 NAT-positive donors may be used for non-lung transplantation. While the long-term allograft outcomes from donors with COVID-19 remain unknown, the decision to recover organs from donors with positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT testing should take into account the recipient’s risk for mortality while remaining on the waitlist and donor factors including severity of illness, time from symptom onset, and organ quality.
Experience regarding outcomes of lung transplantation from SARS-CoV-2 NAT-positive donors is limited at this time. However, one report described successful bilateral lung transplantation in two recipients from donors with a history of COVID-19 >20 days prior to donor evaluation and with positive URT and negative LRT NAT results.25
FIGURE 1
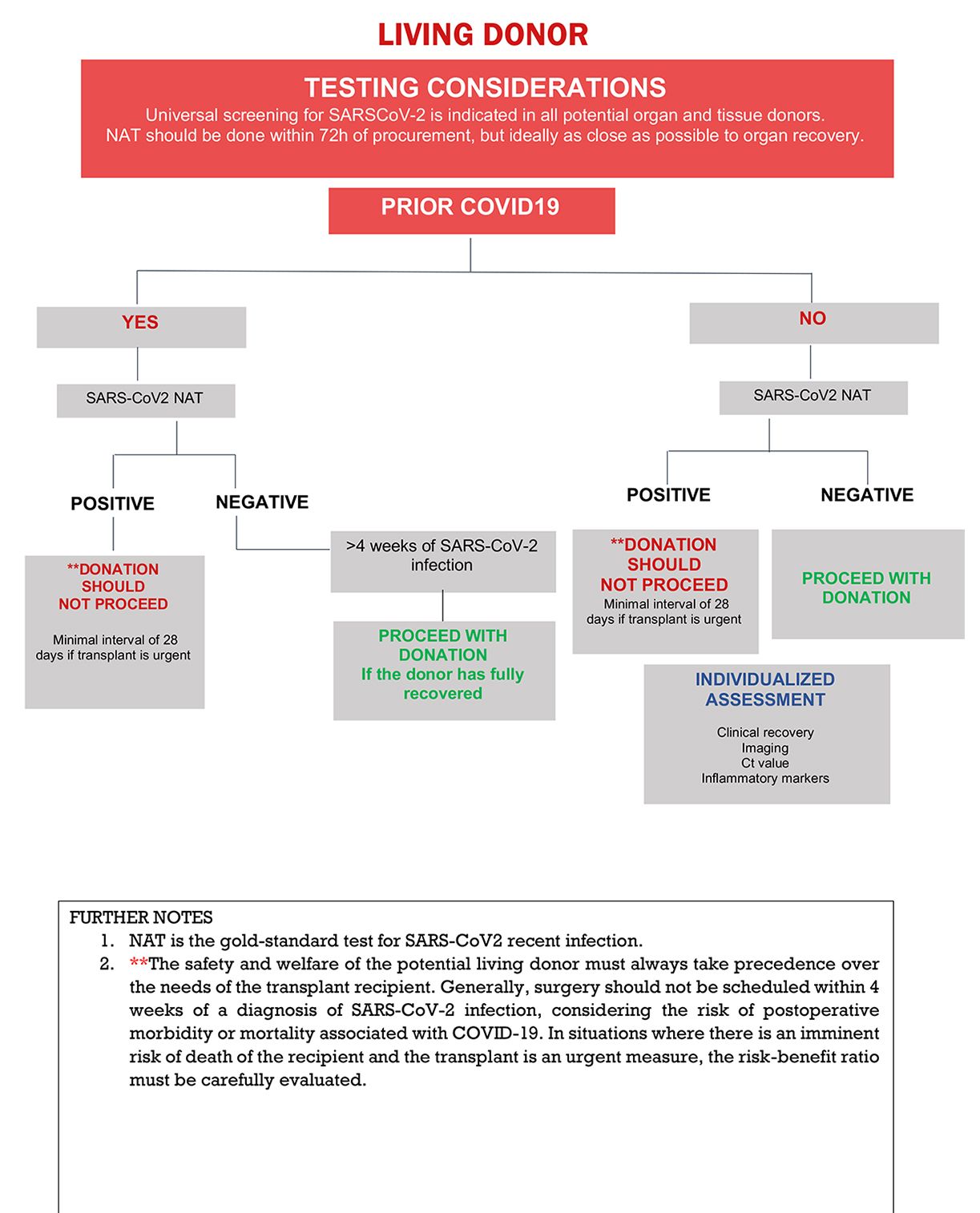
Similar to deceased donors, screening should begin with a review of donor history, including recent exposure to anyone with known or suspected COVID-19, any personal history of COVID-19, including timing of symptom onset and date(s) of previous testing if available, COVID-19 vaccination history, and any symptoms that could be considered consistent with COVID-19 before donation.
It is strongly recommended that all potential living donors are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and maintain stringent precautions as regard to potential exposure to COVID-19 cases until the donation procedure, especially during epidemiological high transmission risk periods in their living areas.
The recommended laboratory assessment of living donors for SARS-CoV-2 infection is outlined in Figure 2. All transplant societies strongly recommend universal screening by NAT of potential organ donors before procurement (Table 1) and recommend that this be performed as close to procurement as possible (less than 72 hours but ideally within 24 hours of procurement).4,26
Donor SARS-CoV-2 testing using serology or antigen detection is not recommended.5
Asymptomatic living donors without recent history of COVID-19, without recent exposures to COVID-19, and negative NAT testing, may proceed with donation.
The safety and welfare of the potential living donor must always take precedence over the needs of the transplant recipient. Previous studies demonstrated an increased risk of adverse outcomes in low-cardiovascular risk unvaccinated patients undergoing elective non-cardiac surgery within the first 7 weeks after recovery.27,28 We note that the two major studies showing higher rates of complications in patients who underwent surgery within the first 4 to 8 weeks of COVID-19 reported data from 2020-2021.28,29 However, a recent retrospective cohort study demonstrated no increased postoperative mortality among vaccinated patients who underwent surgery within four weeks of COVID-19.30 The optimal timing of donation following COVID-19 in the Omicron era remains unclear. In situations where there is an imminent risk of death of the recipient and transplant is urgent, a careful risk-benefit evaluation is called for. For transplant emergencies (eg, fulminant hepatitis) shortening the interval from infection to donation to 28 days might be considered (liver living donors) but to this time there is no available objective data to support this decision.
FIGURE 2
Healthcare workers should adhere to local infection control guidance to minimize the risk of SARS-CoV-2 transmission during organ recovery and transplantation. Even if COVID-19 is not suspected in the donor, eye protection and use of an N95 or equivalent respirator is recommended for aerosol-generating procedures and surgical procedures that may pose a higher risk for transmission if the patient were to have COVID-19.4 Additionally, all healthcare workers should be vaccinated against COVID-19.4
If SARS-CoV-2 infection is confirmed in the recipient, it might be difficult to determine if the infection was donor-derived. Importantly, however, documented transmissions have only occurred in lung transplant recipients whose donors had negative URT but positive LRT NAT results. While limited data regarding small bowel transplantation exist, there is also concern that small bowel transplantation from SARS-CoV-2 NAT-positive donors could result in transmission. Any concern for donor-derived infection should be reported in accordance with local and national requirements so that appropriate investigations may take place.
At this time, it does not appear that recipients of organs from donors with positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT results require pre-emptive antivirals or monoclonal antibody therapy as post-exposure prophylaxis, and it remains unclear whether vaccinated recipients or those with serologic evidence of prior infection should be prioritized to receive organs from donors with a positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT.31
All potential recipients should be made aware of the option to consider accepting an organ from a donor with a positive SARS-CoV2 NAT (a potentially increased-risk donor), and should be informed of the limited information available to this date about the potential of transmission. Ideally, this point should be discussed with the patient at the time of pre-transplant evaluation and appropriate informed consent from potential recipients should be obtained. It is suggested that a standardized informed consent process be used.
Higher rates of post-operative respiratory failure and pneumonia have been reported among those undergoing surgery within 4 weeks of developing COVID-19,29 and there is increased risk of adverse outcomes in patients undergoing elective non-cardiac surgery within 7 weeks of COVID-19 diagnosis.27,28 However, given that transplantation is frequently non-elective and may be the only life-saving treatment possible, candidates with a history of COVID-19 may warrant transplantation within 7 weeks of their diagnosis.
The National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death (NCEPOD) classifies the types of surgery as Emergency, Urgent, Scheduled and Elective. Transplant candidates should undergo a complete evaluation to define the urgency of the procedure. The optimal approach to preoperative transplant screening after COVID-19 is not yet well defined. Expert consensus statements have proposed systematic cardiovascular screening that includes an electrocardiogram, a transthoracic echocardiogram, and measurement of high-sensitivity troponin prior surgery. This recommendation was made in the context of an otherwise healthy population and may not be generalizable to older or comorbid adults undergoing non-cardiac surgery.32 Preoperative screening must be individualized, incorporating the baseline cardiac risk, history of cardiovascular complications of COVID-19, severity of COVID-19 illness, and the clinical status after recovery. Acute phase reactants may remain elevated after COVID19 recovery. It is difficult to establish their value as biomarkers with predictive value for post-operative complications.33
TID recommends at this point that ALL transplant candidates should undergo COVID-19 screening. The approach should include epidemiological screening, such as history of disease or exposure plus chest imaging and SARS-CoV2 testing. In this regard, SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR is considered the gold-standard test for screening of current/recent infection. RATs are not recommended, but if available, recent positive RAT tests should be considered part of the overall evaluation.
The general consensus is that solid organ transplantation is probably safe if the patient had COVID-19 with complete clinical recovery and:
- Mild cases: There is an interval of ≥ 14 days after symptom onset (or initial positive test) AND negative SARS-CoV2- PCR test at the time of the procedure.34
- Severe cases (pneumonia): There is an interval of ≥ 28 days after symptom onset (or initial positive test) AND negative SARS-CoV2- PCR test at the time of the procedure.
If the candidate has experienced clinical resolution within the aforementioned timeframes but SARS-CoV-2 PCR remains positive within 90 days of his or her initial COVID-19 diagnosis, Ct values (when available) and Ct value trend may aid in the decision to proceed with transplantation. Values above 30 usually correlate with absence of complete virions with infective capacity,35 but caution is advised when interpreting Ct values (see Section B above). If follow-up SARS-CoV2 PCRs remain positive, the possibility of reinfection should also be considered. Clinical course, imaging and Ct value may assist the physician with individualized decisions in such cases (Figure 3).
Successful transplantation procedures in recipients with complete clinical recovery after COVID-19, but remaining PCR-positive a few days before36 or at the time of the procedure have been reported.37 However, as above, the decision to proceed (particularly for high urgency candidates) with a transplant procedure should be considered individually for each patient by the transplantation team. Reports describing outcomes among non-lung transplant recipients who underwent transplantation following COVID-19 are outlined in Table 2. Additional considerations regarding thoracic transplantation and liver transplantation are addressed below.
Considerations for Thoracic Transplant Candidates
As above, the optimal timing of transplantation for thoracic transplant candidates with a history of COVID-19 remains unclear. We recommend deferral of transplantation for candidates who present with symptoms compatible with COVID-19 or who have a new positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT at the time of organ offer. Like the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), we recommend that these candidates be reactivated for transplantation upon clinical resolution of COVID-19 symptoms, as applicable, and two successive negative NAT results are obtained 24-48 hours apart, as feasible. However, individualized approaches to reactivation may be warranted in the setting of prolonged viral RNA shedding. In this case, those with a history of COVID-19 may be considered for transplantation provided the following three criteria are met: 1) complete resolution of symptoms as applicable, 2) lack of COVID-19-related end-organ damage, and 3) >14-28 days from the onset of symptoms, considering the risk of the candidate’s waitlist mortality.38
Thorough evaluation is required for patients who may require lung transplantation due to COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. In general, such patients may be listed for transplantation if they are at least 28 days from the onset of severe lung injury and have at least two successive negative NATs obtained at least 24-48 hours apart with at least one specimen being obtained from the lower respiratory tract if possible. For those patients not connected to a ventilator (i.e., on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) and without a tracheostomy, two negative PCR tests from the nasopharynx obtained 24 hours apart may be used to inform the decision to proceed with transplantation. In cases of persistent viral shedding, bilateral lung transplant is recommended. Additional considerations should include patient age, presence of single-organ dysfunction, clinical and radiographic evidence of irreversible respiratory failure, rehabilitation potential, nutritional status, and center experience with high-risk transplantation.38-41
Considerations for Liver Transplant Candidates
Unfortunately, the data are insufficient to definitely conclude that liver transplant (LT) is safe in candidates who have a current positive COVID-19 PCR or RAT or a recent SARS-CoV-2 infection, without increasing risk of postoperative complications, graft loss and death. Some groups have had good results with recipients who had a positive result at time of the transplant.42 On the other hand, despite the uncertainty regarding outcomes, there is no alternative to LT. Liver transplant indication is based on urgency established by mortality scores, such as Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) and Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD). Apart from this, some situations should be prioritized [e.g., hepatorenal syndrome (HRS)], and patients should not have their transplant delayed.43 Similarly, a patient presenting an acute liver failure (ALF) should be taken to transplant, as soon as possible.44
Indications for LT are impacted by age and urgency. For adults, an urgent or semi-urgent procedure will be considered for: acute liver failure, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatorenal syndrome, acute on chronic liver failure, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, severe hepatopulmonary syndrome, decompensated cirrhosis, uncontrollable ascites, recurrent encephalopathy, and early hepatocellular carcinoma. For pediatric patients some conditions are considered for prompt procedure, such as: acute liver failure, hepatopulmonary syndrome, hepatoblastoma, recurrent cholangitis, metabolic crisis in errors of metabolism and decompensated liver disease.43
Recent guidelines of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) noted that many patients with COVID-19 (from mild to severe disease) have successfully undergone organ transplantation during an active infection. AASLD suggests that liver transplantation should be offered to patients with acute liver failure despite COVID-19 infection. Evidence supporting the safety of liver transplantation in these patients with no option for any other treatment, justifies performing this life saving intervention. In this regard, the arguments in favor should take into consideration that a SARS-CoV-2 RNA can remain detectable for weeks after infection and may not always represent active infection, personal protective equipment is effective, and the mortality in these patients is very high without intervention.45 Open communication with the patient (if communicative), the family is critical. Depending on the usual practices of the hospital, the input of the in-house ethics committee may be invoked.
FIGURE 3
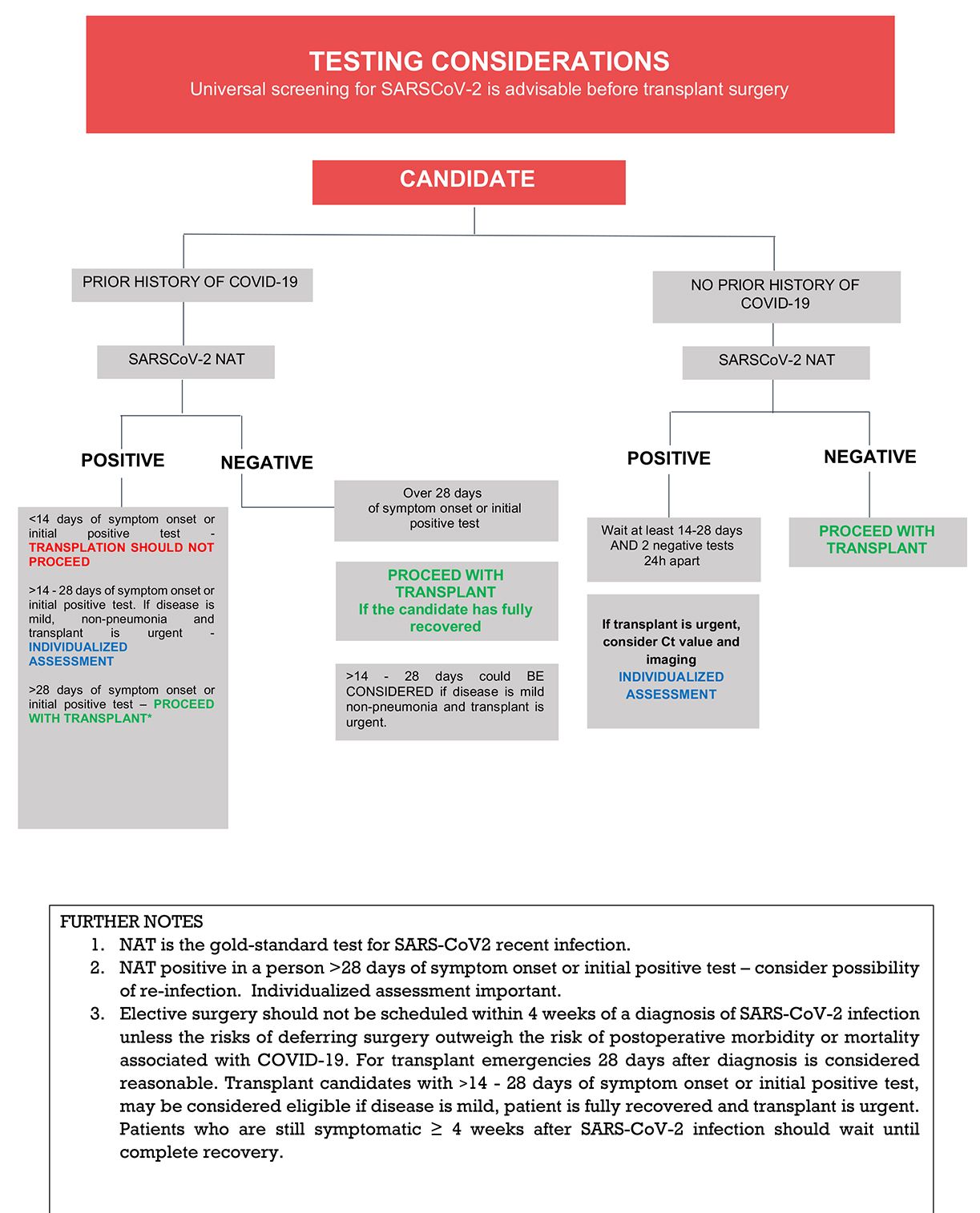
Table 1: International Recommendations For Donor Screening, Testing, and Acceptance
| Region | Institution/date | Candidate | Deceased donor | Living donor | Source of information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | USA - AST | Complete symptom resolution and 2 negative PCR tests at least 24h apart. Usually one month, at least 14 days if transplant is urgent. |
Non-lung transplantation may proceed if the donor has a history of resolved COVID-19 diagnosed >10 days prior or has a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR and no known history | May proceed after symptom resolution and ideally with negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR. | More detailed information on donor testing and organ acceptance and updates regarding AST recommendations may be found at https://www.myast.org/sites/default/files/Education/2022%20Donor%20Testing%20Document.pdf |
| Canada | https://cdtrp.ca/en/covid-19-international-recommendations-for-odt/ Last update April 30, 2021 | ||||
| South America | Brazil - ABTO | Usually one month after positive result | If onset of symptoms > 10 days and < 21 days from the donation date and mild COVID-19 – donor can be accepted (non-lung and intestines) | NOTA TÉCNICA Nº 24/2022-CGSNT/DAET/SAES/MS. Gerenciamento do risco sanitário da epidemia de COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) para a doação e transplantes de órgãos, tecidos e células-tronco hematopoéticas. (March, 2022) Recomendações para Avaliação e Aceite do Doador na Pandemia COVID-19. Liberação de transplantes com doadores COVID positive. COMISSÃO DE INFECÇAO EM TRANSPLANTE. ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE TRANSPLANTE DE ÓRGÃOS. (January, 2022) Clemente WT et al. Recomendações para Avaliação e Aceite do Candidato ao Transplante de Órgãos Sólidos no Contexto da Covid -19. Brazilian Journal of Transplantation, 2022. https://doi.org/10.53855/bjt.v25i3.468_pt (English version available) |
|
| Argentina | Under review | ||||
| Europe | Spain - ONT | Spanish recommendations for the evaluation and selection of donors and recipients regarding covid-19 (the biovigilance alert reference bv-es-20200122 last update 4 April 2022) | |||
| Italy - Centro Nazionale Trapianti | 14 days after negative result in COVID swab | Consider standard donors after 14 days from positive swab and negative BAL at the time of evaluation | |||
| England NHS Blood and Transplant | https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.16577 | ||||
| Australia | Transplantation Society of Australia and New Zealand (TSANZ) | https://tsanz.com.au/storage/COVID_Communiques/OTA-TSANZ-COVID_19_Info_for_donation_and_transplantation_prof_Nov-2021_FINAL.pdf | |||
| Asia | Singapore | Screen all potential donors with URT and LRT sample. Donor exclusion if symptoms <28 days OR < 6 weeks if confirmed COVID19 |
|||
| Thailand | 6 weeks after positive NAT result | Screen all potential donors with a pool testing of URT and LRT sample. Accept non-lung donor if >= 4 weeks from positive test, with a negative repeated PCR, or Ct> 30 Accept lung donor if > 4 weeks from positive test, with a negative repeated PCR |
NAT test by URT sample and accept donors if >= 4 weeks from positive test and repeat PCR shows Ct > 30 | ||
| Israel | RT-PCR testing of URT sample within 24h of retrieval. All lung donors should have an additional negative test result in LRT sample. |
Accept donors with a pneumonia or lower respiratory tract infection with negative test; and donors who had previously tested positive, after a period of 6 weeks and 2 negative repeated tests within 72 h of donation. All potential donors undergo CT scan | Katvan et al, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13584-022-00519-8 |
Table 2: Summary of Non-Lung Transplant Recipients Transplanted after COVID-19
| Patient | COVID Severity | Time elapsed from COVID to Transplantation | PCR-SARS CoV-2 at the time of transplantation | Transplanted organ | Follow up | SARS CoV-2 Serology at transplantation | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mild | 90 days | Negative | Kidney Pancreas | 2 months | IgG+ | Alive | Singh N et al. Kidney Int. 2020 Dec;98(6):1615-1616. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.004. |
| 2 | Mild | 36 days | Negative | Liver | 6 months | IgG+ | Alive | Niess H, et al. Liver transplantation in a patient after COVID-19 - Rapid loss of antibodies and prolonged viral RNA shedding. Am J Transplant. 2021 Apr;21(4):1629-1632. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16349. |
| 3 | Severe | 65 days | Negative | Kidney | 9 months | IgG+ | Alive | Tuschen K, et al Renal transplantation after recovery from COVID-19 - a case report with implications for transplant programs in the face of the ongoing corona-pandemic. BMC Nephrol. 2021 Jul 6;22(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02448-1. |
| 4 | Mild | 60 days | Negative | Kidney | 1 months | NA | Alive | Kijima Y, et al Allogeneic Kidney Transplantation After COVID-19: A Case Report. Transplant Proc. 2021 Oct 15:S0041-1345(21)00744-2. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2021.10.004. |
| 5 | Mild | 44 days | Negative | Kidney | 2 months | IgG+ | Alive | Varotti G, et al. Successful kidney transplantation after COVID-19. Transpl Int. 2020 Oct;33(10):1333-1334. doi: 10.1111/tri.13703. |
| 6 | Severe | 42 days | Negative | Liver | NA | NA | Alive | Raut V,. Successful liver transplantation immediately after recovery from COVID-19 in a highly endemic area. Transpl Int. 2021 Feb;34(2):376-377. doi: 10.1111/tri.13790. |
| 7 | Mild | 71 days | Negative | Liver | 25 days | Negative | Alive | Dhand A, et al. Successful liver transplantation in a patient recovered from COVID-19. Transpl Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;23(2):e13492. doi: 10.1111/tid.13492. |
| 8 | Mild | 17 days | Negative | Liver | 2 months | Alive | Kulkarni AV, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant. 2021 Jun;21(6):2279-2284. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16509. Epub 2021 Feb 15. | |
| 9 | Mild | 15 days | Negative | Liver | 24 days | Died (bacterial sepsis) | Kulkarni AV, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant. 2021 Jun;21(6):2279-2284. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16509. Epub 2021 Feb 15. | |
| 10 | Moderate | 16 days | Negative | Liver | 91 days | IgG+ | Alive | Kulkarni AV, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant. 2021 Jun;21(6):2279-2284. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16509. Epub 2021 Feb 15. |
| 11 | Mild | 16 days | Negative | Liver | 67 days | iGG+ | Alive | Kulkarni AV, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant. 2021 Jun;21(6):2279-2284. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16509. Epub 2021 Feb 15. |
| 12 | Mild | 32 days | Negative | Liver | 63 days | Alive | Kulkarni AV, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant. 2021 Jun;21(6):2279-2284. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16509. Epub 2021 Feb 15. | |
| 13 | Mild | 30 days | Negative | Liver | 56 days | Alive | Kulkarni AV, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant. 2021 Jun;21(6):2279-2284. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16509. Epub 2021 Feb 15. | |
| 14 | Mild | 9 days | Negative | Liver | 12 days | IgG neg/IgM neg | Alive | Martini S, et al Urgent liver transplantation soon after recovery from COVID-19 in a patient with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Hepatol Commun. 2020 Jul 14;5(1):144–5. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1580. |
| 15 | Mild | approx 30 days | positive | Kidney | 40 days | IgG+/IgM + | Alive | Radisic MV et al. Kidney Transplantation in a Recipient with Positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 Int J Organ Transplant Med 2021 (12) 3. (not yet indexed) |
- Loupy A, Aubert O, Reese PP, Bastien O, Bayer F, Jacquelinet C. Organ procurement and transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020;395:e95-e6..
- Galvan NTN, Moreno NF, Garza JE, et al. Donor and transplant candidate selection for solid organ transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic Am J Transplant 2020;20:3113-22
- Bullard J, Dust K, Funk D, et al. Predicting Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 From Diagnostic Samples Clin Infect Dis 2020;71:2663-6.
- Summary of Current Evidence and Information– Donor SARS-CoV-2 Testing & Organ Recovery from Donors with a History of COVID-19. at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/media/kkhnlwah/sars-cov-2-summary-of-evidence.pdf
- Kumar D, Manuel O, Natori Y, et al. COVID-19: A global transplant perspective on successfully navigating a pandemic. Am J Transplant 2020;20:1773-9.
- CR Recommendations for the Use of Chest Radiography and Computed Tomography (CT) for Suspected COVID-19 Infection, 2020. at https://www.acr.org/Advocacy-and-Economics/ACR-Position-Statements/Recommendations-for-Chest-Radiography-and-CT-for-Suspected-COVID19-Infection.
- Koval CE, Poggio ED, Lin YC, Kerr H, Eltemamy M, Wee A. Early success transplanting kidneys from donors with new SARS-CoV-2 RNA positivity: A report of 10 cases. Am J Transplant 2021;21:3743-9
- Romagnoli R, Gruttadauria S, Tisone G, et al. Liver transplantation from active COVID-19 donors: A lifesaving opportunity worth grasping? Am J Transplant 2021;21:3919-25.
- Kumar D, Humar A, Keshavjee S, Cypel M. A call to routinely test lower respiratory tract samples for SARS-CoV-2 in lung donors. Am J Transplant 2021;21:2623-4.
- Puodziukaite L, Serpytis M, Kundrotaite A, et al. Kidney transplantation from a SARS-CoV-2-positive donor for the recipients with immunity after COVID-19. Transpl Infect Dis 2021;23:e13666
- de la Villa S, Valerio M, Salcedo M, et al. Heart and liver transplant recipients from donor with positive SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR at time of transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 2021;23:e13664
- Meshram HS, Kute VB, Patel H, Desai S, Chauhan S, Dave RB. A case report of successful kidney transplantation from a deceased donor with terminal COVID-19-related lung damage: Ongoing dilemma between discarding and accepting organs in COVID-19 era! Transpl Infect Dis 2021;23:e13683.
- Sigler R, Shah M, Schnickel G, et al. Successful heart and kidney transplantation from a deceased donor with PCR positive COVID-19. Transpl Infect Dis 2021;23:e13707
- Frattaroli P, Anjan S, Coro A, et al. Is it safe to perform abdominal transplantation from SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction positive donors? Transpl Infect Dis 2021;23:e13688.
- Manzia TM, Gazia C, Lenci I, et al. Liver transplantation performed in a SARS-CoV-2 positive hospitalized recipient using a SARS-CoV-2 infected donor. Am J Transplant 2021;21:2600-4
- Dhand A, Gass A, Nishida S, et al. Successful transplantation of organs from a deceased donor with early SARS-CoV-2 infection. Am J Transplant 2021;21:3804-5
- Hong HL, Kim SH, Choi DL, Kwon HH. A case of coronavirus disease 2019-infected liver transplant donor. Am J Transplant 2020;20:2938-41.
- Nguyen MC, Lee EJ, Avery RK, et al. Transplant of SARS-CoV-2-infected Living Donor Liver: Case Report. Transplant Direct 2021;7:e721
- Perlin DV, Dymkov IN, Terentiev AV, Perlina AV. Is Kidney Transplantation From a COVID-19-Positive Deceased Donor Safe for the Recipient? Transplant Proc 2021;53:1138-42
- La Hoz RM, Mufti AR, Vagefi PA. Short-term liver transplant outcomes from SARS-CoV-2 lower respiratory tract NAT positive donors. Transpl Infect Dis 2022;24:e13757
- Lee K, Desai NM, Resnick J, et al. Successful kidney transplantation from a deceased donor with severe COVID-19 respiratory illness with undetectable SARS-CoV-2 in donor kidney and aorta. Am J Transplant 2022;22:1501-3
- Schold JD, Koval CE, Wee A, Eltemamy M, Poggio ED. Utilization and outcomes of deceased donor SARS-CoV-2-positive organs for solid organ transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant 2022
- Bock MJ, Vaughn GR, Chau P, Berumen JA, Nigro JJ, Ingulli EG. Organ transplantation using COVID-19-positive deceased donors. Am J Transplant 2022
- Danziger-Isakov LA GJ, Woolley A, Pouch SM, et al. . Organs from Donors with Positive SARS-CoV-2 NAT Testing: A Report from the Ad Hoc Disease Transmission Advisory Committee Oral abstract presented at the 2022 American Transplant Congress
- Eichenberger EM, Coniglio AC, Milano C, et al. Transplanting thoracic COVID-19 positive donors: An institutional protocol and report of the first 14 cases. J Heart Lung Transplant 2022
- Katvan E, Cohen J, Ashkenazi T. Organ donation in the time of COVID-19: the Israeli experience one year into the pandemic-ethical and policy implications. Isr J Health Policy Res 2022;11:6
- Rohatgi N, Smilowitz NR, Reejhsinghani R. Perioperative Cardiovascular Considerations Prior to Elective Noncardiac Surgery in Patients With a History of COVID-19. JAMA Surg 2022;157:187-8
- Collaborative CO, GlobalSurg C. Timing of surgery following SARS-CoV-2 infection: an international prospective cohort study. Anaesthesia 2021;76:748-58
- Deng JZ, Chan JS, Potter AL, et al. The Risk of Postoperative Complications After Major Elective Surgery in Active or Resolved COVID-19 in the United States. Ann Surg 2022;275:242-6
- Le ST, Kipnis P, Cohn B, Liu VX. Covid-19 Vaccination and the Timing of Surgery Following Covid-19 Infection. Ann Surg 2022
- Eichenberger EM, Kaul DR, Wolfe CR. The pandemic provides a pathway: What we know and what we need to know about using COVID positive donors. Transpl Infect Dis 2021;23:e13727
- ASA and APSF Joint Statement on Elective Surgery/Procedures and Anesthesia for Patients after COVID-19 Infection. 2022. at https://www.asahq.org/about-asa/newsroom/news-releases/2022/02/asa-and-apsf-joint-statement-on-elective-surgery-procedures-and-anesthesia-for-patients-after-covid-19-infection.
- ASilvapulle E, Johnson D, Darvall JN. Risk stratification of individuals undergoing surgery after COVID-19 recovery. Br J Anaesth 2022;128:e37-e9
- Kulkarni AV, Parthasarathy K, Kumar P, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: The first report. Am J Transplant 2021;21:2279-84
- Berg MG, Zhen W, Lucic D, et al. Development of the RealTime SARS-CoV-2 quantitative Laboratory Developed Test and correlation with viral culture as a measure of infectivity. J Clin Virol 2021;143:104945
- Rouphael C, D'Amico G, Ricci K, et al. Successful orthotopic liver transplantation in a patient with a positive SARS-CoV2 test and acute liver failure secondary to acetaminophen overdose. Am J Transplant 2021;21:1312-6
- Radisic MV, Walther JC, Werber G, et al. Kidney Transplantation in a Recipient with Positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2. Int J Organ Transplant Med 2021;12:42-7
- Guidance from the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation regarding the SARS CoV-2 pandemic. 2021. at https://ishlt.org/ishlt/media/documents/SARS-CoV-2_Guidance-for-Cardiothoracic-Transplant-and-VAD-center.pdf.
- Cypel M, Keshavjee S. When to consider lung transplantation for COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:944-6
- Ghodsizad A, Grant AA, Mohammed AN, et al. Bilateral pneumonectomy and lung transplant for COVID-19 induced respiratory failure. JTCVS Tech 2022
- Lang C, Jaksch P, Hoda MA, et al. Lung transplantation for COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome in a PCR-positive patient. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:1057-60
- Arias-Murillo YR, Benavides VC, Salinas NM, Osorio-Arango K, Plazas-Sierra C, Cortes JA. SARS-CoV2/COVID-19 Infection in Transplant Recipients and in Patients on the Organ Transplant Waiting List in Colombia. Transplant Proc 2021;53:1237-44
- Gupta S, Sudhindran S, Saraf N, et al. Liver Transplant Society of India Guidelines for Liver Transplant During COVID-19 times. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2022;12:180-5
- Yohanathan L, Campioli CC, Mousa OY, et al. Liver transplantation for acute liver failure in a SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive patient. Am J Transplant 2021;21:2890-4
- Nickerson AM, Sobotka LA, Kelly SG. PRO: Liver Transplantation in the Times of COVID-19: "To Transplant or Not to Transplant". Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2021
Contact
Address
Transplant Infectious Disease
c/o The Transplantation Society
740 Notre-Dame Ouest
Suite 1245
Montréal, QC, H3C 3X6
Canada


