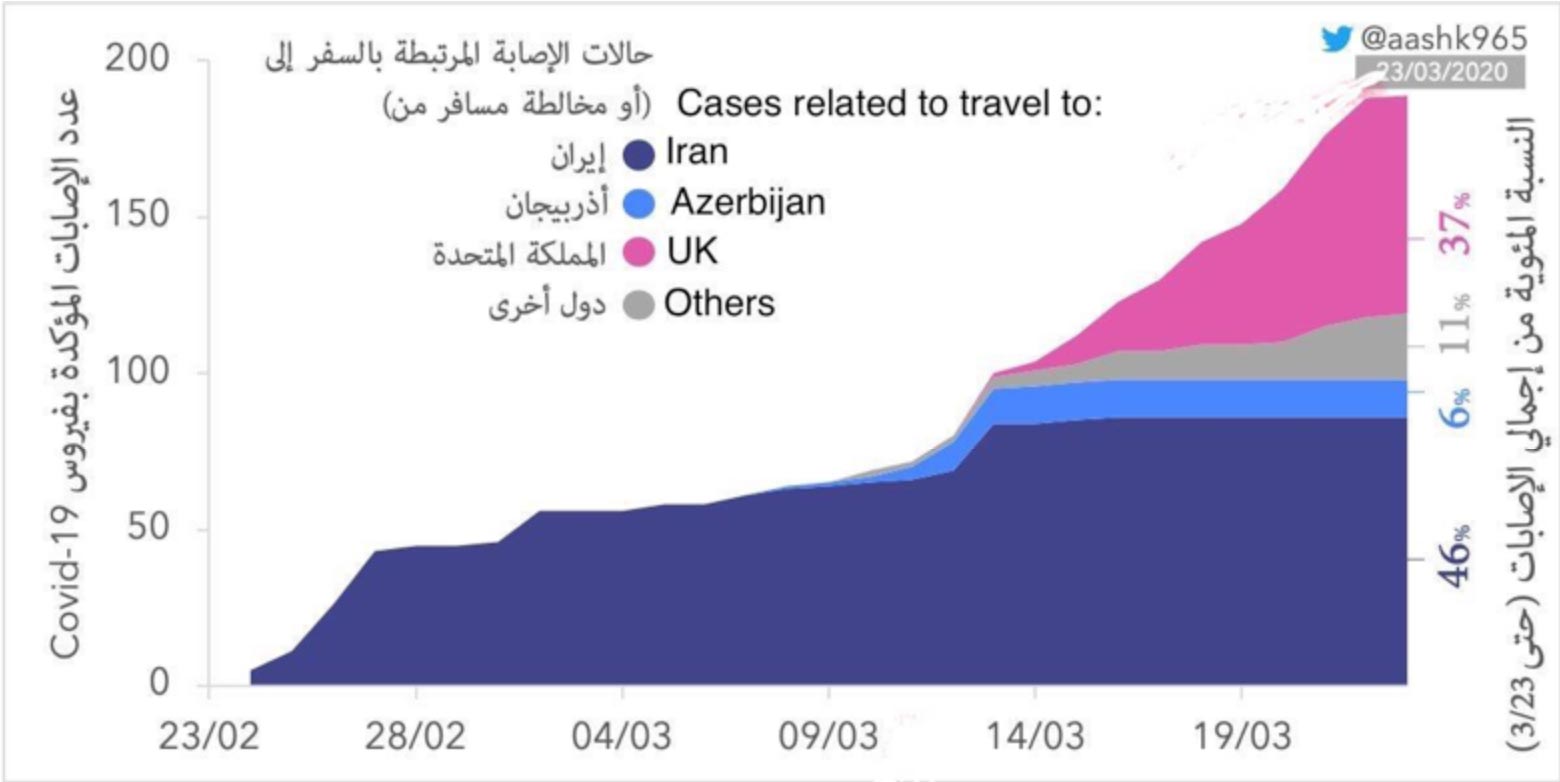
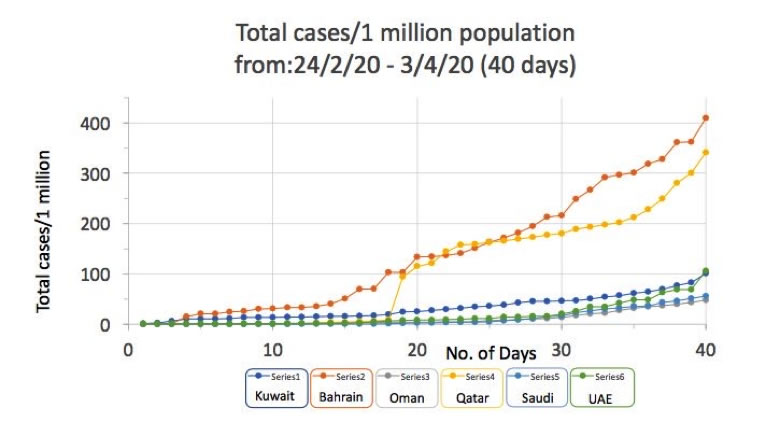
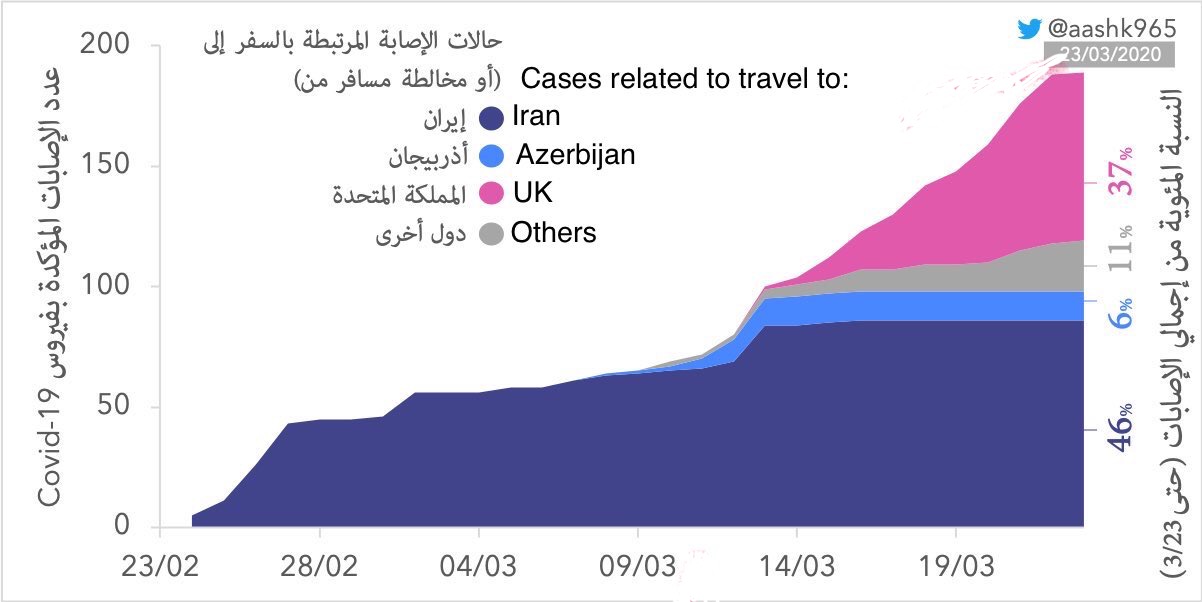
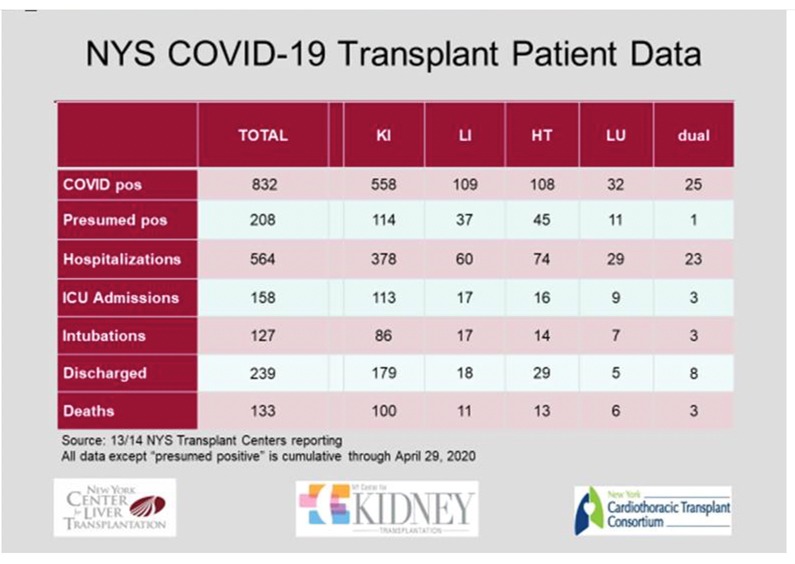
COVID-19 Updates
In response to the Covid-19 pandemic, The Transplantation Society has created this COVID-19 Dashboard to serve as a resource for transplant professionals to get up to date information about the pandemic.
The Covid-19 Committee is meeting multiple times a week, working together to address the needs of the international transplant community as the situation unfolds.
If you are a Transplant Professional and you have questions to ask the committee or, would like to contribute valuable information to the Dashboard - Kindly email covid-19@tts.org.
TTS Resources

Mortality rates in Transplant recipients infected with SARSCov2 and diagnosed as having COVID-19. April 2020
There has been a global assumption that transplant recipients would be particularly endangered by the current pandemic of Coronovirus. Data have however been quite sparse and the ability to create a global picture has been limited.
Case reports are now giving way to small case series in the literature. The Transplantation Journal has collected the following data from correspondents from around the world and offers it as a very limited and highly flawed view of what might be happening.
Data from New York centres has been supplied from New York and are presented separately as they provide the most comprehensive view of the increased risk of death for transplant recipients across the spectrum of organ transplant types. The story of a widespread tragedy in the field of Transplantation is not underestimating the current data. Careful inspection of the data could be seen to show two features:
- High mortality rates in the range of 15-30% for transplant recipients in the countries and regions with high incidences and high mortality rates in the general populations.
- Low incidence and no mortality for transplant recipients in low incidence countries, suggesting that transplant recipients may have heeded well the messages to isolate themselves from the virus.
Country |
COVID pos |
alive In ICU |
Dead |
Mongolia |
0 |
0 |
0 |
New Zealand |
0 |
0 |
0 |
India (5 States) |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Denmark |
2 |
0 |
1 |
Singapore |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Hong Kong |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Brazil |
27 |
3 |
7 |
Korea |
2 |
0 |
0 |
Australia |
3 |
0 |
0 |
USA |
9 |
1 |
0 |
Italy |
20 |
4 |
5 |
Strasbourg |
48 |
10 |
9 |
London |
7 |
4 |
1 |
Totals |
120 |
22 |
23 |
(All data reports above are at the time of reporting in April)


June 17
Verma, S.; Aleen Agarwal, S.; Chikkala, B. R.; Dey, R.; Singh, S.; Varma, S.; Yadav, V.; Das, D.; Goyal, S.; Pandey, V. K.; Nasa, V.; Madan, K.; Shweta, S.; Tarai, B.; Gupta, S.
American Journal of Transplantation. 2020;[record in progress]
The concerns in Living Donor Liver Transplant (LDLT) are that immunosuppressed recipients and healthy donors would be exposed to nosocomial SARS‐ CoV‐2 infection. However, as described in this paper from a tertiary center in India, as patients began to suffer and die; LDLT was allowed for those who were very sick, or had just recovered from a life threatening decompensation (high MELD/ CTP score) or had malignancy.
Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Kidney and Liver Transplant Patients: A Single-Center Experience.
Aydincan Akdur, Emre Karakaya, Ebru H. Ayvazoglu Soy, Omar Alshalabi, Mahir Kirnap, Hande Arslan, Gaye Ulubay, Koray Hekimoglu, Gokhan Moray, Mehmet Haberal
Experimental and Clinical Transplantation (2020) 3: 270-274
This article included 583 transplant patients (509 kidney and 74 liver) who were screened at a single transplant center in Turkey between March 1 and May 1, 2020. 18 patients had respiratory symptoms and only one patient diagnosed with COVID-19.
COVID-19 in elderly kidney transplant recipients.
Marta Crespo, María José Pérez-Sáez, Dolores Redondo-Pachón, Laura Llinàs-Mallol, María Milagro Montero, Judith Villar, Carlos Arias-Cabrales, Anna Buxeda, Carla Burballa, SusanaVázquez, Thais López, Fátima Moreno, Marisa Mir, Sara Outón, Adriana Sierra, Silvia Collado, Clara Barrios, Eva Rodríguez, Laia Sans, Francesc Barbosa, Higini Cao, María Dolores Arenas, Roberto Güerri-Fernández, Juan Pablo Horcajada, Julio Pascual
American Journal of Transplantation 2020 doi: 10.1111/AJT.16096
This article describes 16 kidney transplant recipients over age of 65 with COVID-19. 33% showed renal graft dysfunction. Short-term fatality rate was 50% at a median time since admission of 3 days. Those who died were more frequently obese, frail and had underlying heart disease. Patients who died were more anemic, lymphopenic and showed higher D-dimer, C-reactive protein, and IL-6 at their first tests.
Umberto Maggiore, Daniel Abramowicz, Marta Crespo, Christophe Mariat, Geir Mjoen, Licia Peruzzi, Mehmet Sükrü Sever, Gabriel C Oniscu, Luuk Hilbrands, Bruno Watschinger on behalf of the DESCARTES Working Group of the ERA-EDTA
This article reviews previous published studies of kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 and discusses current treatment options.
Rapid generation of neutralizing antibody responses in COVID-19 patients.
Mehul S. Suthar, Matthew G. Zimmerman, Robert C. Kauffman, Grace Mantus, Susanne L. Linderman, William H. Hudson, Abigail Vanderheiden, Lindsay Nyhoff, Carl W. Davis, Seyi Adekunle, Maurizio Affer, Melanie Sherman, Stacian Reynolds, Hans P. Verkerke, David N. Alter, Jeannette Guarner, Janetta Bryksin, Michael Horwath, Connie M. Arthur, Natia Saakadze, Geoffrey Hughes Smith, Srilatha Edupuganti, Erin M. Scherer, Kieffer Hellmeister, Andrew Cheng, Juliet A. Morales, Andrew S. Neish, Sean R. Stowell, Filipp Frank, Eric Ortlund, Evan Anderson, Vineet D. Menachery, Nadine Rouphael, Aneesh Mehta, David S. Stephens, Rafi Ahmed, John D. Roback, Jens Wrammert
Cell Reports Medicine. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100040
This article reports a cross-sectional study of antibody responses to the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein and virus neutralization activity in a cohort of 44 hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The RBD-specific binding data were further validated in a clinical setting with 231 PCR-confirmed COVID-19 patient samples. These findings have implications for understanding protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2, therapeutic use of immune plasma, and development of much-needed vaccines.
June 11
Ling Li, MD, PhD
JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10044
Published online June 3, 2020.
This is an open-label, multicenter, randomized clinical trial performed in 7 medical centers in Wuhan, China. The trial included 103 participants with laboratory confirmed COVID-19 that was severe (respiratory distress and/or hypoxemia) or life-threatening (shock, organ failure, or requiring mechanical ventilation). Convalescent plasma in addition to standard treatment (n = 52) vs standard treatment alone (control) (n = 51), stratified by disease severity. There was no significant difference in 28-day mortality (15.7%vs 24.0%; OR, 0.65 [95%CI, 0.29-1.46]; P = .30. Convalescent plasma treatment was associated with a negative conversion rate of viral PCR at 72 hours in 87.2%of the convalescent plasma group vs 37.5% of the control group (OR, 11.39 [95%CI, 3.91-33.18]; P < .001).Convalescent plasma therapy added to standard treatment, compared with standard treatment alone, did not result in a statistically significant improvement in time to clinical improvement within 28 days.
COVID-19 in liver transplant recipients: preliminary data from the ELITA/ELTR registry.
Luca S Belli, Christophe Duvoux, Vincent Karam, Rene Adam, Valentin Cuervas-Mons, Luisa Pasulo, Carmelo Loinaz, Federica Invernizzi, Damiano Patrono, Sherrie Bhoori, Olga Ciccarelli, Maria Cristina Morelli, Lluis Castells, Victor Lopez-Lopez, Sara Conti, Costantino Fondevila, Wojchiech Polak
Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Jun 4
This is a report about the course and management of SARS-CoV-2 infection in 10 liver transplant recipients from a single center in Northwestern Italy in the period March-April 2020. Overall mortality was 20%, whereas Covid-related mortality was 10%.
Husain SA, Dube G, Morris H, Fernandez H, Chang JH, Paget K, Sritharan S, Patel S, Pawliczak O, Boehler M, Tsapepas D, Crew RJ, Cohen DJ, Mohan S.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 May 18:CJN.05170420
The study describes an early cohort of outpatient kidney transplant recipients with known or suspected coronavirus disease 2019, of which many had symptomatic resolution without requiring hospitalization.
COVID-19 and kidney transplantation: an Italian Survey and Consensus.
Vistoli F, Furian L, Maggiore U, Caldara R, Cantaluppi V, Ferraresso M, Zaza G, Cardillo M, Biancofiore G, Menichetti F, Russo A, Turillazzi E, Di Paolo M, Grandaliano G, Boggi U; Italian National Kidney Transplantation Network; the Joint Committee of the Italian Society of Organ Transplantation and the Italian Society of Nephrology.J Nephrol. 2020 Jun 3. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00755-8. Online ahead of print.
Based on the Italian experience, the authors discuss the reasons for the changes in kidney transplantation activity during the COVID-19 pandemic in Western countries. They also provide working recommendations for the organization and management of kidney transplantation under these conditions. Overall, 60 recipients tested positive for SARS-CoV2 infection, 57 required hospitalization, 17 were admitted to the ICU, and 11 died.
The Innate Immune System: Fighting on the Front Lines or Fanning the Flames of COVID-19?
Julia L. McKechnie, Catherine A. Blish
Cell Host Microbe. 2020 May 20 doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.009 [Epub ahead of print]
PMCID: PMC7237895
In this review, the authors discuss what is known about the role of the innate immune system during SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggest directions for future studies, and evaluate proposed COVID-19 immunomodulating therapeutics.
The effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the COVID-19 pandemic
Hsiang, S., Allen, D., Annan-Phan, S. et al.
Nature (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2404-8
This article compiles new data on 1,717 local, regional, and national non-pharmaceutical interventions deployed in the ongoing pandemic across localities in China, South Korea, Italy, Iran, France, and the United States. In the absence of policy actions, the authors estimated that early infections of COVID-19 exhibit exponential growth rates of roughly 38% per day. It is estimated that across these six countries, interventions prevented or delayed on the order of 62 million confirmed cases, corresponding to averting roughly 530 million total infections.
June 4
COVIDSurg Collaborative*
LANCET May 29, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31182-X
This is an international, multicentre, cohort study at 235 hospitals in 24 countries included all patients undergoing surgery who had SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed within 7 days before or 30 days after surgery. This article analyzes 1128 patients who had surgery between Jan 1 and March 31, 2020, of whom 835 (74·0%) had emergency surgery and 280 (24·8%) had elective surgery. SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed preoperatively in 294 (26·1%) patients. 30-day mortality was 23·8%. Pulmonary complications occurred in 51·2% of the patients; 30-day mortality in these patients was 38·0%. The authors reported risk factors for mortality.
Xavier Muller et al.
American Journal of Transplantation First published: 31 May 2020
https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.16082
This article reports strategies and preliminary results in liver transplantation during the peak of the SARS‐CoV‐2 pandemic from a single‐center in France. The authors performed 10 successful liver transplantations during the peak of the pandemic with a short median intensive care unit stay (2,5 days), benchmark post‐transplant morbidity and no occurrence of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection during follow‐up.
Matthew J Cummings, Matthew R Baldwin, Darryl Abrams, Samuel D Jacobson, Benjamin J Meyer, Elizabeth M Balough, Justin G Aaron,
Jan Claassen, LeRoy E Rabbani, Jonathan Hastie, Beth R Hochman, John Salazar-Schicchi, Natalie H Yip, Daniel Brodie, Max R O’Donnell
LANCET May 19, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2
This article reviewed 1150 adults who were admitted to between March 2 and April 1, 2020, with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, of which 257 (22%) were critically ill. As of April 28, 2020, 39% patients had died, 79% patients received invasive mechanical ventilation, 31% received renal replacement therapy. Older age, chronic heart and lung disease, high IL6 and D-dimer levels were associated with mortality.
Anakinra for severe forms of COVID-19: a cohort study.
Thomas Huet, Hélène Beaussier, Olivier Voisin, Stéphane Jouveshomme, Gaëlle Dauriat, Isabelle Lazareth, Emmanuelle Sacco, Jean-Marc Naccache, Yvonnick Bézie, Sophie Laplanche, Alice Le Berre, Jérôme Le Pavec, Sergio Salmeron, Joseph Emmerich, Jean-Jacques Mourad, Gilles Chatellier, Gilles Hayem
Lancet Rheumatol 2020 Published Online May 29, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30164-8
This article reports 52 consecutive patients in the anakinra group and 44 historical patients who were identified in the Groupe Hospitalier Paris Saint-Joseph COVID cohort study from March 24 to April 6, 2020. Admission to the ICU for invasive mechanical ventilation or death occurred in 13 (25%) patients in the anakinra group and 32 (73%) patients in the historical group (hazard ratio [HR] 0・22 [95% CI 0・11–0・41; p<0・0001). The treatment effect of anakinra remained significant in the multivariate analysis (HR 0・22 [95% CI 0・10–0・49]; p=0・0002).
Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19.
Quan-Xin Long et al.
Nature Medicine
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0897-1
This article reports acute antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in 285 patients with COVID-19. Within 19 days after symptom onset, 100% of patients tested positive for antiviral immunoglobulin-G (IgG). Seroconversion for IgG and IgM occurred simultaneously or sequentially. Both IgG and IgM titers plateaued within 6 days after seroconversion. Serological testing may be helpful for the diagnosis of suspected patients with negative RT–PCR results and for the identification of asymptomatic infections.
May 27
Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19.
Maximilian Ackermann, M.D., Stijn E. Verleden, Ph.D., Mark Kuehnel, Ph.D., Axel Haverich, M.D., Tobias Welte, M.D., Florian Laenger, M.D., Arno Vanstapel, Ph.D., Christopher Werlein, M.D., Helge Stark, Ph.D., Alexandar Tzankov, M.D., William W. Li, M.D., Vincent W. Li, M.D., Steven J. Mentzer, M.D., and Danny Jonigk, M.D.
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432
This article examined lungs from 7 autopsies to try to better understand the pathophysiology of the progressive respiratory failure that leads death in Covid-19 infection. In Covid-19 patients the histological finding was a diffuse alveolar damage with perivascular T-cell infiltration, associated to severe endothelial, intracellular virus and disrupted cell membranes, together with widespread thrombosis and microangiopathy. Covid-19 patients had also intussusceptive angiogenesis, which it is a distinctive from equally severe influenza virus infection.
Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19— Preliminary Report.
J.H. Beigel, K.M. Tomashek, L.E. Dodd, A.K. Mehta, B.S. Zingman, A.C. Kalil, E. Hohmann, H.Y. Chu, A. Luetkemeyer, S. Kline, D. Lopez de Castilla, R.W. Finberg, K. Dierberg, V. Tapson, L. Hsieh, T.F. Patterson, R. Paredes, D.A. Sweeney, W.R. Short, G. Touloumi, D.C. Lye, N. Ohmagari, M. Oh, G.M. Ruiz‑Palacios, T. Benfield, G. Fätkenheuer, M.G. Kortepeter, R.L. Atmar, C.B. Creech, J. Lundgren, A.G. Babiker, S. Pett, J.D. Neaton, T.H. Burgess, T. Bonnett, M. Green, M. Makowski, A. Osinusi, S. Nayak, and H.C. Lane, for the ACTT-1 Study Group Members*
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
This is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of intravenous remdesivir in adults hospitalized with Covid-19 with evidence of lower respiratory tract involvement. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (200 mg loading dose on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for up to 9 additional days) or placebo for up to 10 days. Preliminaryresults from the 1059 patients (538 assigned to remdesivir and 521 to placebo) indicated that those who received remdesivir had a median recovery time of 11 days (95% confidence interval [CI],9 to 12), as compared with 15 days (95% CI, 13 to 19) in those who received placebo. The Kaplan- Meier estimates of mortality by 14 days were 7.1% with remdesivir and 11.9% with placebo (hazard ratio for death, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.47 to 1.04).
Mandeep R Mehra, Sapan S Desai, Frank Ruschitzka, Amit N Patel
Lancet. Published on lime May 22, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(20)31180-6
This article did a multinational registry analysis of the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19. 96032 patients (mean age 53·8 years, 46·3% women) with COVID-19 were hospitalised during the study period and met the inclusion criteria. Of these, 14 888 patients were in the treatment groups (1868 received chloroquine, 3783 received chloroquine with a macrolide, 3016 received hydroxychloroquine, and 6221 received hydroxychloroquine with a macrolide) and 81 144 patients were in the control group. Each of these drug regimens was associated with decreased in-hospital survival and an increased frequency of ventricular arrhythmias when used for treatment of COVID-19.
Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19.
Daniel Blanco-Melo, Benjamin E. Nilsson-Payant, Wen-Chun Liu, Skyler Uhl, Daisy Hoagland, Rasmus Møller, Tristan X. Jordan, Kohei Oishi, Maryline Panis, David Sachs, Taia T. Wang, Robert E. Schwartz, Jean K. Lim, Randy A. Albrecht, and Benjamin R. tenOever
Cell 181, 1–10, May 28, 2020 ª 2020 Elsevier Inc.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026
This article documented an in-depth analysis of the transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 compared with other respiratory viruses. Cell and animal models of SARS-CoV-2 infection, in addition to transcriptional and serum profiling of COVID-19 patients, consistently revealed a unique and inappropriate inflammatory response. This response is defined by low levels of type I and III interferons juxtaposed to elevated chemokines and high expression of IL-6.
Alba Grifoni, Daniela Weiskopf, Sydney I. Ramirez, Jose Mateus, Jennifer M. Dan, Carolyn Rydyznski Moderbacher, Stephen A. Rawlings, Aaron Sutherland, Lakshmanane Premkumar, Ramesh S. Jadi, Daniel Marrama, Aravinda M. de Silva, April Frazier, Aaron Carlin, Jason A. Greenbaum,
CELL 11420
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.015
Using HLA class I and II predicted peptide ‘megapools’, circulating SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were identified in ~70% and 100% of COVID-19 convalescent patients, respectively. CD4+ T cell responses to spike, the main target of most vaccine efforts, were robust and correlated with the magnitude of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA titers. The authors detected SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD4+ T cells in ~40-60% of
unexposed individuals, suggesting cross-reactive T cell recognition between circulating ‘common cold’ coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2.
Feng-Cai Zhu, Yu-Hua Li, Xu-Hua Guan, Li-Hua Hou, Wen-Juan Wang, Jing-Xin Li, Shi-Po Wu, Bu-Sen Wang, Zhao Wang, Lei Wang, Si-Yue Jia, Hu-Dachuan Jiang, Ling Wang, Tao Jiang, Yi Hu, Jin-Bo Gou, Sha-Bei Xu, Jun-Jie Xu, Xue-Wen Wang, Wei Wang, Wei Chen
Lancet May 2020
https://doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(20)31208-3
This is a dose-escalation, single-centre, open-label, non-randomised, phase 1 trial of an Ad5 vectored COVID-19 vaccine in Wuhan, China. 108 participants (51% male, 49% female; mean age 36·3 years) were recruited and received the low dose (n=36), middle dose (n=36), or high dose (n=36) of the vaccine. ELISA antibodies and neutralising antibodies increased significantly at day 14, and peaked 28 days post-vaccination. Specific T-cell response peaked at day 14 post-vaccination.
May 20
Organ procurement and transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Loupy A, Aubert O, Reese PP, Bastien O, Bayer F, Jacquelinet C.
Lancet. 2020 May 11. pii: S0140-6736(20)31040-0. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31040-0. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
PMID: 32407668
This article documented a 90.6% reduction in deceased donor transplantations since the COVID-19 outbreak in France and 51.1% in the USA, respectively.
Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages.
Merad M, Martin JC.
Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4. [Epub ahead of print] Review.
PMID: 32376901
This article describes potentially pathological roles of macrophages during SARS- CoV-2 infection and discusses ongoing and prospective therapeutic strategies to modulate macrophage activation in patients with COVID-19.
COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients.
Nair V, Jandovitz N, Hirsch JS, Nair G, Abate M, Bhaskaran M, Grodstein E, Berlinrut I, Hirschwerk D, Cohen SL, Davidson KW, Dominello AJ, Osorio GA, Richardson S, Teperman LW, Molmenti EP.
Am J Transplant. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15967. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32351040
This article reports 30% mortality and 50% acute kidney injury in 10 kidney transplant recipients.
Covid-19 in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases - Case Series from New York.
Haberman R, Axelrad J, Chen A, Castillo R, Yan D, Izmirly P, Neimann A, Adhikari S, Hudesman D, Scher JU.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
PMID: 32348641
This article identified 86 patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disease who had either confirmed (59 patients) or highly suspected (27 patients) symptomatic Covid-19 infection. 62 of 86 (72%) were receiving biologics or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and the overall incidence of hospitalization was 16%.
Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab.
Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, Fu B, Zhou Y, Zheng X, Yang Y, Li X, Zhang X, Pan A, Wei H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 29. pii: 202005615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005615117. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32350134
This is a retrospective, uncontrolled study of 21 patients with severe COVID-19 who received treatment with the IL-6 blocker tocilizumab. Within 24 hours of starting tocilizumab therapy, fevers and elevated C-reactive protein levels resolved, and levels of IL-6 and other proinflammatory cytokines declined. All patients subsequently were discharged alive.
Characteristics and Outcomes of Recipients of Heart Transplant With Coronavirus Disease 2019.
Latif F, Farr MA, Clerkin KJ, Habal MV, Takeda K, Naka Y, Restaino S, Sayer G, Uriel N.
JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 13. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2159. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32402056
This article describes case series of 28 patients who had received heart transplant in a large academic center. The mortality rate was 25% and 76% had evidence of myocardial injury. Mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in 16 patients (70%), and 6 (26%) had a reduction in the dose of their calcineurin inhibitor. Treatment of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (78%), high-dose corticosteroids (47%), and interleukin 6 receptor antagonists (26%).
May 13
This week's selection made by: Enver Akalin, Marlies Reinders, Pablo Uva, Nithya Krishnan, Manisha Sahay, Shannon Grappe and Annmarie Liapakis
Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: Emerging Evidence of a Distinct Pathophysiology.
Batlle D, Soler MJ, Sparks MA, Hiremath S, South AM, Welling PA, Swaminathan S; COVID-19 and ACE2 in Cardiovascular, Lung, and Kidney Working Group.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 May 4.
This article emphasizes that AKI can be a severe complication of COVID-19 and the importance of assessing, defining, and reporting the course of AKI is highlighted.
Immediate impact of COVID-19 on transplant activity in the Netherlands.
de Vries APJ, Alwayn IPJ, Hoek RAS, van den Berg AP, Ultee FCW, Vogelaar SM, Haase-Kromwijk BJJM, Heemskerk MBA, Hemke AC, Nijboer WN, Schaefer BS, Kuiper MA, de Jonge J, van der Kaaij NP, Reinders MEJ.
Transpl Immunol. 2020 May 1:101304.
This article describes the enormous impact of COVID-19 on transplant activity in the Netherlands. There was a significant decrease in organ donation numbers affecting all organ transplant services and detrimental effect on transplantation numbers in children with end-organ failure. The paper also describes ongoing efforts focus on mitigation of not only primary but also secondary harm of the pandemic and to find right definitions and momentum to restore the transplant programs.
Elens L, Langman LJ, Hesselink DA, Bergan S, Moes DJAR, Molinaro M, Venkataramanan R, Lemaitre F.
Ther Drug Monit. 2020 Apr 15.
This article inform the clinicians about the potential interactions of experimental COVID-19 treatments with immunosuppressive drugs used in transplantation. Recommendations regarding therapeutic drug monitoring and dose adjustments in the context of COVID-19 are provided.
Shah MB, Lynch RJ, El-Haddad H, Doby B, Brockmeier D, Goldberg DS.
Am J Transplant. 2020 May 5
This article presents a review of the current literature that details the potential negative consequences of COVID-19 positive donors. The authors concluded that COVID-19 infection should continue to remain a contraindication for donation, as has been the initial response of donation and transplantation societies.
Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19.
Geleris J, Sun Y, Platt J, Zucker J, Baldwin M, Hripcsak G, Labella A, Manson D, Kubin C, Barr RG, Sobieszczyk ME, Schluger NW.
N Engl J Med. 2020 May 7.
This observational study involving 1446 patients with Covid-19 who had been admitted to the hospital documented that hydroxychloroquine administration was not associated with either a greatly lowered or an increased risk of the composite end point of intubation or death.
May 6
This week's selection made by: Enver Akalin, Marcelo Cantarovich and Medhat Askar
Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: Emerging Evidence of a Distinct Pathophysiology.
Batlle D, Soler MJ, Sparks MA, Hiremath S, South AM, Welling PA, Swaminathan S; COVID-19 and ACE2 in Cardiovascular, Lung, and Kidney Working Group.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 May 4.
This article emphasizes that AKI can be a severe complication of COVID-19 and the importance of assessing, defining, and reporting the course of AKI is highlighted.
Immediate impact of COVID-19 on transplant activity in the Netherlands.
de Vries APJ, Alwayn IPJ, Hoek RAS, van den Berg AP, Ultee FCW, Vogelaar SM, Haase-Kromwijk BJJM, Heemskerk MBA, Hemke AC, Nijboer WN, Schaefer BS, Kuiper MA, de Jonge J, van der Kaaij NP, Reinders MEJ.
Transpl Immunol. 2020 May 1:101304.
This article describes the enormous impact of COVID-19 on transplant activity in the Netherlands. There was a significant decrease in organ donation numbers affecting all organ transplant services and detrimental effect on transplantation numbers in children with end-organ failure. The paper also describes ongoing efforts focus on mitigation of not only primary but also secondary harm of the pandemic and to find right definitions and momentum to restore the transplant programs.
Elens L, Langman LJ, Hesselink DA, Bergan S, Moes DJAR, Molinaro M, Venkataramanan R, Lemaitre F.
Ther Drug Monit. 2020 Apr 15.
This article inform the clinicians about the potential interactions of experimental COVID-19 treatments with immunosuppressive drugs used in transplantation. Recommendations regarding therapeutic drug monitoring and dose adjustments in the context of COVID-19 are provided.
Shah MB, Lynch RJ, El-Haddad H, Doby B, Brockmeier D, Goldberg DS.
Am J Transplant. 2020 May 5
This article presents a review of the current literature that details the potential negative consequences of COVID-19 positive donors. The authors concluded that COVID-19 infection should continue to remain a contraindication for donation, as has been the initial response of donation and transplantation societies.
Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19.
Geleris J, Sun Y, Platt J, Zucker J, Baldwin M, Hripcsak G, Labella A, Manson D, Kubin C, Barr RG, Sobieszczyk ME, Schluger NW.
N Engl J Med. 2020 May 7.
This observational study involving 1446 patients with Covid-19 who had been admitted to the hospital documented that hydroxychloroquine administration was not associated with either a greatly lowered or an increased risk of the composite end point of intubation or death.
April 29
This week's selection made by: Enver Akalin, Milagros Samaniego-Picota and Gabriel Gondolesi. The article tites are hyperlinks
Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review.
Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB.
JAMA. 2020 Apr 13. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6019. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32282022
This is a review regarding pharmacologic treatment of patients with COVID-19. Currently, there is no evidence from randomized clinical trials that any potential therapy improves outcomes inpatients with either suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW; and the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium, Barnaby DP, Becker LB, Chelico JD, Cohen SL, Cookingham J, Coppa K, Diefenbach MA, Dominello AJ, Duer-Hefele J, Falzon L, Gitlin J, Hajizadeh N, Harvin TG, Hirschwerk DA, Kim EJ, Kozel ZM, Marrast LM, Mogavero JN, Osorio GA, Qiu M, Zanos TP.
JAMA. 2020 Apr 22. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6775. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32320003
Clinical outcomes were assessed for 2634 patients who were discharged or had died at the study end point. During hospitalization, 373 patients (14.2%) (median age, 68 years [IQR, 56-78]; 33.5% female) were treated in the intensive care unit care, 320 (12.2%) received invasive mechanical ventilation, 81 (3.2%) were treated with kidney replacement therapy, and 553 (21%) died. Mortality for those requiring mechanical ventilation was 88.1%.
Covid-19 and Kidney Transplantation.
Akalin E, Azzi Y, Bartash R, Seethamraju H, Parides M, Hemmige V, Ross M, Forest S, Goldstein YD, Ajaimy M, Liriano-Ward L, Pynadath C, Loarte-Campos P, Nandigam PB, Graham J, Le M, Rocca J, Kinkhabwala M.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2011117. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
PMID: 32329975
Montefiore Medical Center reported clinical outcomes of 36 consecutive adult kidney transplant recipients. 28 patients (78%) required hospital admission. Twenty-seven (96%) of hospitalized patients had imaging findings of viral pneumonia, 11(39%) required mechanical ventilation and 6 (21%) required renal replacement therapy. Mortality was 10 (28%) overall, 7 (64%) in intubated patients, with a median follow-up of 21 days (range 14-28).
Alberici F, Delbarba E, Manenti C, Econimo L, Valerio F, Pola A, Maffei C, Possenti S, Piva S, Latronico N, Focà E, Castelli F, Gaggia P, Movilli E, Bove S, Malberti F, Farina M, Bracchi M, Costantino EM, Bossini N, Gaggiotti M, Scolari F; Brescia Renal COVID Task Force.
Kidney Int Rep. 2020 Apr 4. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.04.001. [Epub ahead of print] Review.
PMID:32292866
Italian experience in 20 kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 pneumonia documented a fast progression in more than 75% of their patients with 25% mortality during a median follow-up of 7 days.
Early Impact of COVID-19 on Transplant Center Practices and Policies in the United States.
Boyarsky BJ, Chiang TP, Werbel WA, Durand CM, Avery RK, Getsin SN, Jackson KR, Kernodle AB, Van Pilsum Rasmussen SE, Massie AB, Segev DL, Garonzik-Wang JM.
Am J Transplant. 2020 Apr 13. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15915. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32282982
This article reports the early impact of COVID-19 on transplant Center Practices and Policies in the US. Complete suspension of living-donor kidney transplant activity was reported by 71.8%, and living-donor liver transplant activity by 67.7%. Suspension of deceased-donor transplant activity was less frequent with restrictions for kidney donors in 84% and for liver donors by 73%, associated with the regional incidence of COVID-19.
Fix OK, Hameed B, Fontana RJ, Kwok RM, McGuire BM, Mulligan DC, Pratt DS, Russo MW, Schilsky ML, Verna EC, Loomba R, Cohen DE, Bezerra JA, Reddy KR, Chung RT.
Hepatology. 2020 Apr 16. doi: 10.1002/hep.31281. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32298473
In this article, the AASLD expert panel propose detailed guidelines for diagnosis and management of COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver disease and liver transplant recipients including donor and recipient selection recommendations during the pandemic.
COVID-19 in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Initial Report from the US Epicenter.
Pereira MR, Mohan S, Cohen DJ, Husain SA, Dube GK, Ratner LE, Arcasoy S, Aversa MM, Benvenuto LJ, Dadhani D, Kapur S, Dove LM, Brown RS, Rosenblatt RE, Samstein B, Uriel N, Farr MA, Satlin M, Small CB, Walsh T, Kodiyanplakkal RP, Miko BA, Aaron JG, Tsapepas DS, Emond JC, Verna EC.
Am J Transplant. 2020 Apr 24. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15941. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32330343
This article reports 90 transplant recipients (46 were kidney recipients, 17 lung, 13 liver, 9 heart and 5 dual-organ transplants) at 2 centers in New York. Among the 68 hospitalized patients, 12% required non-rebreather and 35% required intubation. Sixteen patients died (18% overall, 24% of hospitalized, 52% of ICU) and 37 (54%) were discharged.
COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: a single-center case series from Spain.
Fernández-Ruiz M, Andrés A, Loinaz C, Delgado JF, López-Medrano F, San Juan R, González E, Polanco N, Folgueira MD, Lalueza A, Lumbreras C, Aguado JM.
Am J Transplant. 2020 Apr 16. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15929. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32301155
This article reports preliminary experience with 18 SOT (kidney [44.4%], liver [33.3%] and heart [22.2%]) recipients diagnosed with COVID-19. The mortality rate was 27.8%.
Interactive Maps
Registries & Surveys
The Pediatric Infectious Disease Society through the PIDTRAN network of pediatric ID practitioners is collecting ALL COVID-19 cases in Pediatrics in the US including those with and without immunocompromising conditions.
We encourage all pediatrics groups to work with their infectious disease colleagues to report each case only once.
We invite you/your center to participate. We are asking you to contribute de-identified information about any COVID-19 case in pediatric patients, inpatient or outpatient, diagnosed or treated at your center.
This survey is for ALL pediatric patients less than 21 years of age in the USA, including:
- General Pediatric patients, with or without other co-morbidities
- Immunocompromised pediatric patients
- Transplant and cellular therapy recipients
To submit a case via the electronic survey forms, click here or copy and paste the following url: redcap.stjude.org/surveys/?s=37F8JCEWR8
What you need to know:
- St. Jude Children's Research Hospital IRB has approved this study and has determined that other sites providing non-HIPAA identifiable clinical data for this project are NOT considered to be engaged in human subjects research. Your role in the project does NOT require local IRB approval at your site, but please refer to your local policies and procedures. (please see attached documentation that can be shared with your local IRB if needed.)
- This is an initial survey for the first 7 days of COVID-19 illness. A follow-up survey forms should be completed once the patient has reached Day 28 post Covid-19 diagnosis. We will send you an email with the link to complete the follow-up survey forms once you have submitted the initial survey.
- We hope that individuals within each institution will work together so that cases are only entered once.
- Sites will be asked to record the REDCap assigned subject ID for each patient they submit. This subject ID will be available on the electronic survey. We have attached a log to track to use as a tool for tracking patients; however, you may use whatever tracking method you prefer. This log is not to be shared with anyone outside of your site. Please maintain your patient tracking linking the patient to the REDCap ID until notified that the study has been completed.
- We encourage you to share this invitation with your colleagues at other institutions!
Please contact PIDTRANCoordinators@STJUDE.ORG with any questions.
Shared on behalf of the PIDSTRAN team and Gabriela Maron (St. Jude Children's Research Hospital).
Lara Danziger-Isakov, MD, MPH
Professor of Pediatrics
Director, Immunocompromised Host Infectious Diseases
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
The Society of Pediatric Liver Transplantation (SPLIT), a section of TTS, and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) have partnered to create a secure and de-identified online pediatric registry (for patients under the age of 21 years). Our intention is to collect and disseminate the experience of our community to better understand the clinical presentation, natural history and long-term outcomes in our hepatology and liver and intestinal transplant population. We are requesting all clinicians worldwide to report all cases of COVID -19 in children with chronic liver diseases (still with native liver), listed for pediatric liver/intestine transplantation, or have undergone liver and/or intestinal transplantation.
We encourage you to complete this form even if the patient is in the middle of their COVID-19 course. This allows for timely dissemination back to our community. A weekly summary of COVID cases will be reported on the SPLIT COVID listserv, the NASPGHAN GI listserv and the NASPGHAN COVID website.
To submit a case, please use this link or copy and paste the following url: https://is.gd/naspghansplitliversurvey
Thank you to everyone in our community that is coming together at this time and for your efforts to serve our hepatology and transplant patients and support each other. Sincerely,
- Mohit Kehar, Pediatric Gastroenterologist and Hepatologist, Queens University
- Mercedes Martinez, Chair of the NASPGHAN Hepatology Committee and Medical Director of Intestinal Transplantation, Columbia University
- Noelle Ebel, Transplant Hepatologist, Stanford University
- Steven Lobritto, Chair of the SPLIT Quality Improvement and Clinical Care Committee, Medical Director of Pediatric Liver Transplantation, Columbia University
- Vicky Ng, SPLIT President and Medical Director of Pediatric Liver Transplantation, University of Toronto
This study has been granted REB/IRB clearance according to the recommended principles of Queen's University and Columbia University.

SARS-CoV-2 infection has been a challenge for health systems worldwide, causing a dramatic consumption of resources to cope with this pandemic caused by this recently identified virus. Solid information about SARS-CoV-2 (from a pathophysiological, clinical and therapeutic point of view) is scarce. On many occasions, these questions have been answered based on available knowledge from similar viruses such as SARS-CoV and MERS.
Due to the potential severity of this disease and the absence of current tools able to definitively modify its natural history, many are the ongoing research works that have been started since the description of the first case of COVID-19. Currently, our clinical practice in this type of infection is based on data especially from retrospective studies whose scientific power is questionable and which, on many occasions, provide contradictory messages.
These handicaps associated with the management and knowledge of COVID-19 extend, even with a greater lack of knowledge, to the population of recipients of a solid organ transplant (SOT) and to organ donation protocols, which have been adapted (in occasions drastically) to this new scenario. However, again, the data that supports these protocols and the available evidence on the management of organ donation and the recipient of a SOT are, likewise, of little scientific solidity.
As a result of this absence of solid evidence that allows for a significant improvement in the management of this risk population, The International Database on Organ donation and Transplantation – COVID19 (IDOTCOVID) has been designed. The present database tries to exhaustively collect the demographic, clinical, analytical and therapeutic data that of SOT recipients with COVID-19 and, afterwards, to extrapolate large-scale conclusions to provide reliable information and, more importantly, to guide in a solid way the future management of this population.
One of the main objectives of this project is the development of a tool that helps in the management of immunosuppression and the treatment of COVID19 infection in SOT recipients.
To achieve this, the following objectives have been designed to be developed in stages and progressively:
- Creation of an international database that includes all SOT recipient patients with COVID19 infection (confirmed or suspected);
- Inclusion of different clinical and analytical data with recognized prognostic factor in the general population;
- Inclusion of treatment data, including management of immunosuppression and clinical outcomes;
- Development of a Machine Learning algorithm that can assist the scientific community in updating their treatment management and immunosuppression protocols in this high-risk population;
COVID 19 in Solid Organ Transplant: Initial Report.
Step 1:
Download and read the following required PDF document:
200403-UW-registry.pdf
Step 2:
Access the registry page:
Click here to access
Global Resources
| Dedicated COVID-19 Page | Website |
| Useful Links | Website |
| Video - COVID-19 and transplantation by ILTS ID and Liver Transplantant SIG, worldwide update on COVID-19 status by Vanguard Committee COVID-19 – The State of Affairs in Individual Countries across the Globe, presented by ILTS Vanguard Committee members | Video |
FAQs , For Children with Solid Organ Transplant or Heart Failure
What Parents Should Know - Check out everything you need to know when it comes to keeping your loved one safe during this pandemic! Why am I Staying Home?
WHO YouTube Channel with daily updates and live press briefings
Click here to visit
Main COVID-19 Page
Click here to visit
- Critical preparedness, readiness and response actions for COVID-19
- National laboratories
- Risk communication and community engagement
- Early investigation protocols
- Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Country-level coordination, planning, and monitoring
- Clinical care
- Operational support and logistics
- Virus origin/Reducing animal-human transmission
- Humanitarian operations, camps and other fragile settings
- Surveillance, rapid response teams, and case investigation
- Infection protection and control / WASH
- Guidance for schools, workplaces & institutions
- Points of entry / mass gatherings
- Health workers
- Maintaining Essential Health Services and Systems
| Global | A Doctor Explains How to Make the Safest Face Mask A doctor explains how to make the safest face mask. This is a safe face mask that if built properly should be donated to your local emergency services. It utilizes a HEPA filter, which is much, much better than a cotton mask. | Website | |
| Can DIY Masks Protect Us from Coronavirus? DIY masks to protect against from viruses sounds like a crazy idea. Data shows masks work incredibly well, and they’re also really cheap. Surgical masks cost a few pennies, and they’re capable of filtering out 80% of particles down to 0.007 microns (14 times smaller than the coronavirus). | |||
| Video: making a make-shift face shield using a surgical mask and plastic sheet | |||
| Global | DIY N95 Face Mask | No Sew + Printable Template | Coronavirus | Covid-19 Note - This mask is not intended to replace a N95 mask. It will not protect you at the same level, but it is better than nothing | Website | |
| Global | Home-Made N95 Mask Note - This mask is not intended to replace a N95 mask. It will not protect you at the same level, but it is better than nothing | Website | |
| Global | Hongkongers make reusable fabric masks as Covid-19 epidemic leads to shortages and sky-high prices | Play Video | |
| Global | Instructional video for sewing a child sized mask (COVID-19) Note - This mask is not intended to replace a N95 mask. It will not protect you at the same level, but it is better than nothing | Website | |
| Global | Instructional video for sewing the Olson mask (COVID-19) Learn how to sew a face mask with a filter pocket to insert filter material into the middle of the mask. Find the full sewing tutorial and free PDF pattern download here: https://leahday.com/pages/how-to-make-a-face-mask-free-pattern Note - This mask is not intended to replace a N95 mask. It will not protect you at the same level, but it is better than nothing. UPDATE - The PDF pattern has been updated to include tie instructions as well as elastic. I know most stores are out of thin elastic so I've updated the downloadable PDF pattern to use shoelaces to tie the mask to your face. New UPDATE - The PDF pattern has been updated again to include a child sized mask. One size fits all ages. I've also included washing, filter, and frequently asked questions to the pattern too. Please share this video and free sewing pattern. Please make masks and contact your local medical centers to learn where you can donate masks. Don't forget the VA hospitals, nursing homes, urgent care, and Hospice. | Website | |
Regional Updates & Resources
| Southern African | Southern African Transplantation Society Position Statement and Patient Information | Website |
| Algeria | Ministry of Health Coronavirus COVID-19 page | Website |
| Ethiopia | Ethiopian Public Health Institute | Website |
| Kenya | Ministry of Health | Website |
| Libya | Government website | Website |
| Mali | Malian Ministry of Health | Website |
| Morocco | Ministry of Health COVID Page | Website |
| Nigeria | April 7 - COVID-19 Sub-Saharan Africa Update In most centres in Sub-Saharan Africa, we do not do emergency transplantation. Most common organ transplanted is Kidney. Most centres in countries that have transplant service offer living donation apart from centres in South Africa that also offer deceased donor transplantation. Presently, transplant centres have suspended transplant activities. The RRT patients are being advised on how to protect themselves. Some do tele-consulting to keep up with management of patients. The acute and most cogent problem for transplant patients in some countries is difficulty with sourcing their medications with all borders closed. The international community and governments need to do something urgently about this! I am informed that one of our transplant patients who came back to Nigeria from Europe recently died in hospital where he presented at the A&E Dept acutely ill. He was confirmed to have died from COVID 19. | |
| Nigeria | Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) Coronavirus information | Website |
| Nigeria | COVID-19 Updates from the Federal Government of Nigeria Coronavirus information | Website |
| South Africa | Department of Health COVID-19 Corona Virus South African Resource Portal | Website |
| South Africa | Government of South Africa The National Coronavirus Command Council has decided to enforce a nation-wide lockdown for 21 days with effect from midnight on Thursday 26 March. | Website |
| South Africa | South African Ministry of Health Recent public presentation on the virus epidemiology | Play Video |
| South Africa | South African Tissue Bank Association Position Statement | Website |
| South Africa | Transplantation Journal March Update
The South African population have varying levels of economic development; however, a large percentage belong to the low- and middle-income population groups. With the onset of COVID-19 in our country, we are especially concerned about the resources available, specifically in the state sector hospitals. Unfortunately, in South Africa, there is a poorly and unevenly structured health care service: 85% of our population is depending on the state sector for medical care, but the resources are mostly situated in the private sector. In large parts of the country we have limited ICU capacity and ventilators and therefore we are currently making contingency plans for critically ill patients. The availability of transplantation services are also constrained by the availability of specialist physicians and surgeons and pathology facilities. Transplant services in the state sector have stopped. In the private sector there is still capacity for transplant services, but this is limited by a lack of deceased donors. In the Western Cape most donors come from the state sector hospitals, resulting in a lack of organs available for transplantation. Living donation has come to a complete standstill in South Africa. Deceased transplantation will continue to take place in facilities that have enough staff and infrastructure available. In most state hospitals this is not possible or feasible, due to a lack of deceased donors and health care resources. We are currently trying to reduce our outpatient workload and concentrating on discharging non urgent cases from the hospital. South Africa is locking down as of 25 March 2020 and nobody will be allowed to travel. All restaurants have been closed and only essential services are taking place. | |
| Sudan | Federal Ministry of Health | Website |
| Tunisia | Ministère de la santé publique Coronavirus COVID-19 page | Website |
| Uganda | Ministry of Health | Website |
| China | Guidelines for organ donation and transplantation in China during the outbreak of new coronavirus pneumonia (adopted on February 23, 2020) . This article (available in english and simplified Chinese) will be published in the Journal of Organ Transplant, No. 11, 2020, no. 179-184 (published on 15 March). Author: Chinese Medical Association Organ Transplant Association. Download PDF in Orginal Language (simplified Chinese) | |||||||||||||
| China | Hong Kong - Transplantation Journal April 6 Update Submitted by Nancy Kwan Man
In response to the COVID-19 outbreak, general infection control measures in the Hong Kong public health system include universal masking in all hospitals and clinics, routine temperature screening and travel history checking for all hospital visitors. Febrile patients were managed in segregated area. From mid-March onwards, medical staff who return from overseas travel have been instructed to refrain from going to their workplace for 14 days and undergo self-isolation at home. | |||||||||||||
| China | Hong Kong - Transplantation Journal April 8 Update Submitted by Dr Maggie Ma (Vice President of HKST) on behalf of the Hong Kong Society of Transplantation
Hong Kong experiences a surge of COVID-19 since mid-March as there was huge influx of Hong Kong Resident (including students and traveler) returning back to Hong Kong after the global pandemic. As of 8 April 2020, there are total of 960 confirmed COVID-19 cases and 4 deaths. We initiate early anti-viral treatment irrespective of symptomatology and adjust the anti-viral regime according to viral titre. Whether such approach contributes to the low mortality in Hong Kong requires further studies.
DDKT: deceased donor kidney transplantation; LDKT : living donor kidney transplantation; DDLT: deceased donor liver transplant; LDLT: living donor liver transplantation | |||||||||||||
| China | Hong Kong - Transplantation Journal March Update
As of March, 25th, 2020, there have been 410 cases of COVID 19 in Hong Kong with a population of just under 8 million. Since the first outbreak in January 2020, we saw an initial surge in the number of infections by mid-February 2020 after the Chinese New Year, followed by a rapid decline in the number of cases from late February to early March (averaging 2-3 cases per day). However, with the recent global increase, we have seen a huge influx of returning local residents to Hong Kong. As a result, we are now witnessing a second surge in the number of new cases with over 100 new cases reported just within one week. | |||||||||||||
| China | Shanghai - Transplantation Journal - April 4 2020 Update
China Shanghai, April 4 2020 | |||||||||||||
| China | Wuhan - Transplantation Journal March Update
Compared with a total number of 67000 cases of COVID-19 in Hubei Province, only total of 22 cases were confirmed in organ transplant recipients. There were 19 kidney and 3 liver transplant patients diagnosed since the day of Wuhan’s closure on January 23. We believe this is largely due to years of health follow-up education for transplant recipients. Transplant patients have a better sense of self-protection especially wearing masks during intense influenza seasons. This provides additional evidence that transplant patients can protect themselves from infection with SARS-COV-2 using distancing, masking, hand washing and self isolating measures, even though their immunity is lower than normal. | |||||||||||||
| China | Wuxi - Transplantation Journal - April 4 2020 Update
China, Wuxi Update 4th April 2020 | |||||||||||||
| India | Government of India COVID-19 Update page | Website | ||||||||||||
| India | Government of India April 14 - PM Narendra Modi's address to the nation on COVID-19 | Play Video | ||||||||||||
| India | Indian Society of Transplantation (ISOT) ISOT Transplant Specific Guidelines During COVID-19 Outbreak | |||||||||||||
| India | Mumbai - Transplantation Journal April 6 Update Submitted by Shrirang Bichu, Bombay Hospital, Mumbai
On March 24, 2020 Government of India ordered a country wide complete curfew lockdown for 21 days. Interstate borders are sealed except for essential supplies. Complete cordoning of smaller areas where COVID 19 patients were detected, is being carried out to contain the infection. The official count of confirmed cases as of today is 3374 with 77 deaths. Four states - Maharashtra, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Delhi have been affected much more than the others. The first case in India was detected at around the same time as was in Italy. Although it could argued that the comparatively smaller numbers in India is a result of selected testing, even in the city like Mumbai with a population of 20 million and having the largest number of cases in the country (454 as of today), we do not find intensive care units burdened with COVID-19 patients and only a handful of cases are on ventilatory support in the city. It is too early to say what the impact of the virus pandemic will be in India. The trends in the next two weeks will be crucial to understand this while the current lockdown ends in 9 days with no further plans announced yet. The lockdown has severely affected routine medical services and only emergency services are offered by all hospitals. | |||||||||||||
| India | North West - Transplantation Journal March Update
India took relatively early steps by stopping air traffic with affected countries and had limited the inflow of passengers to only returning Indian citizens together with airlifting of stranded Indian citizens in affected countries with COVID-19 testing prior to travel or on arrival and with strict quarantine. | |||||||||||||
| India | South - Transplantation Journal March Update Indians stranded across the world have been evacuated, quarantined, tested and discharged when negative. Southern states, such as Kerala & Tamilnadu have shut down domestic borders, temperature tests are done to screen those in cars and trains and the Government has just ordered a nationwide lockdown. Schools & universities have shut, so are swimming pools, gyms, malls and movie theatres. Weddings and other public gatherings are banned. There has been an increase in the number of the research labs approved for testing for coronavirus. Government directives and guidelines have been released to provide for measures and infrastructure changes to hospitals to tackle the expected explosion in cases coming. Private & public sector hospitals are gearing up with stringent screening measures, emergency room triage areas, dedicated isolated COVID-19 floors with beds & ICU. Healthcare workers are being trained to work efficiently and safely during the crisis. Any optimism needs to be tempered. The sobering thought that if, in fact the low incidence of disease to date, the small number of patients in Intensive care and the limited mortality above observed in India to date are wrong, then India with its archaic public health system, one of the lowest per capita ICU bed ratios in the world, lack of adequately trained personnel and a large impoverished rural and slum population, will hopelessly careen towards a catastrophic health crisis. It will be an economic and social disaster, from which India might takes decades to recover. | |||||||||||||
| Indonesia | Badan Nasional Penanggulangan Bencana Website Resmi Gugus Tugas Percepatan Penanganan COVID-19 | Website | ||||||||||||
| Indonesia | Ministry of Health Coronavirus information | Website | ||||||||||||
| Indonesia | National Disaster Management Authority COVID-19 Accelerated Handling Task Force Website | Website | ||||||||||||
| Japan | Cabinet Secretariat Coronavirus information - Japan | Website | ||||||||||||
| Japan | Japan Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare Coronavirus advisory information | Website | ||||||||||||
| Japan | Ministry of health press releases | Website | ||||||||||||
| Japan | Transplantation Journal March Update
The country is seeing a steadily increasing number of patients each day. Testing capacity is increasing, but remains insufficient. The Japanese Society for Transplantation published a guideline on March 6th 2020 aiming to prevent transmission from donors and prevent infection of recipients as well as protect medical professionals. | |||||||||||||
| Kazakhstan | Government website | Website | ||||||||||||
| Kyrgyzstan | Ministry of Health website | Website | ||||||||||||
| Malaysia | Ministry of Health Coronavirus information | Website | ||||||||||||
| Mongolia | Government of Mongolia COVID-19 updates (In Mongolian) | Website | ||||||||||||
| Mongolia | Ulaanbaatar - Transplantation Journal March Update We postponed living donor transplantations in March, with the exception of one Liver transplantation at national cancer center on Friday 13 March. To prevent transplant patients being at risk from the general public, follow up of patients is occurring on Saturdays and in clinics isolated from general hospital care. Transplant coordinators are communicating through doctors in the provinces to reduce intercity travel visits and as much consulting is being done through the phone with both primary care doctors and patients. As of today, due to international flight restrictions, we now have very limited supplies of some immunosuppresant drugs. | |||||||||||||
| Nepal | Nepal Ministry of Health and Population COVID-19 updates | Website | ||||||||||||
| Pakistan | Main Government Page Includes COVID-19 Updates | Website | ||||||||||||
| Pakistan | National Institute of Health (NIH) COVID-19 Update page | Website | ||||||||||||
| Papua New Guinea | National Department of Health CORONAVIRUS DISEASE 2019 (COVID-19) OUTBREAK | Website | ||||||||||||
| Philippines | Department of Health COVID-19 Update page | Website | ||||||||||||
| Singapore | Transplantation Journal March Update
Singapore took early measures to screen and isolate suspected COVID-19 cases from Jan 2nd 2020. Hospitals were at heightened vigilance setting up multidisciplinary command centers, creating capacity in emergency departments and isolation wards, implementing mandatory “mask up“ at healthcare facilities, developing contact tracing teams and setting up acute respiratory tract infection wards to accommodate patients with respiratory tract infections who would then be screened for COVID-19. Singapore opened the National Centre for Infectious Disease (NCID) in September 2019 which is a 330 bedded hospital that is equipped to handle highly contagious diseases like Ebola and SARS. As a result, most of the COVID-19 patients have been admitted to the NCID. By January 23rd 2020, Singapore had diagnosed its first confirmed case in a tourist from Wuhan. Restrictions were imposed on the number of visitors in the hospital who had to fill up a declaration form that they are free from COVID-19 risk factors, thermal scanners were set up at hospital entrances with registration of visitors. Elective procedures, including living kidney donor transplants, were postponed and clinics were downsized or rescheduled. Virtual clinics with remote monitoring have replaced physical interviews and counselling, and home delivery of medications facilitated. | |||||||||||||
| Singapore | Ministry of Health April 14 - Singapore remains in "critical situation" amid rise in COVID-19 cases: Health Minister | Play Video | ||||||||||||
| Singapore | Ministry of Health Updates on local situation | Website | ||||||||||||
| Singapore | Prime Minister's Office, Singapore April 14 - PM Lee Hsien Loong's Intervention at the Special ASEAN Summit on COVID-19 | Play Video | ||||||||||||
| South Korea | Ministry of health Guidance for self-quarantine patients | Website | ||||||||||||
| South Korea | Ministry of health Briefing of Central Disaster and Safety Countermeasure Headquarters on COVID-19 | Website | ||||||||||||
| South Korea | Transplantation Journal March Update
South Korea is one of the earliest country which experienced COVID-19 outbreak. Up to 25th March, 357,896 have been tested and 9,137 diagnosed as COVID-19 positive. Detection of new patients peaked at 28th Feb, which was 813 new patients on the day. Since 12th March, the number of new patients has been under 200, so the cumulative growth curve has flattened. 6,456 positive patients were in Daegu city and 1,262 patients were in Kyungpook province. To date 131 patients have died, yielding a mortality rate of 1.43%. The early explosion of COVID-19 occurred through a cult religious group - Shincheonji allowing a focus of COVID-19 screening which detected affected patients even among asymptomatic people. The heavily affected area of Daegu and Kyungpook has suffered from a shortage of hospital beds. Rigorous testing of 20,000 people a day in 633 sites with positive patient isolation enabled rapid control. | |||||||||||||
| Taiwan | Taiwan Centers for Disease Control Coronavirus information | Website | ||||||||||||
| Thailand | Ministry of Public’s Health English-language COVID-19 page for updates on the situation in Thailand | Website | ||||||||||||
| Uzbekistan | Government of Uzbekistan Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan | Website | ||||||||||||
| Vietnam | Ministry of Health Coronavirus information | Website | ||||||||||||
| Europe | ERA-EDTA - useful information on COVID-19 in renal patients including transplant recipients. COVID-19: Information on Registry Initiatives | Website |
| Europe | European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and supply of substances of human origin in theEU/EEA | |
| Europe | European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)pandemic: increased transmission in the EU/EEAand the UK–sixth update | |
| Europe | European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
The COVID-19 pandemic is rapidly evolving, and outbreak investigations are ongoing. ECDC is closely monitoring this outbreak, providing risk assessments, public health guidance, and advice on response activities to EU Member States and the EU Commission. | Website |
| Europe | European Commission Coronavirus response - Joint statement of the Members of the European Council (March 26 ) | Website |
| Europe | European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) EBMT recommendation on: CORONAVIRUS DISEASE COVID-19 | |
| Europe | European Society of Transplantation | Website |
| Europe | Policy Eurotransplant | Website |
| Austria | Federal Ministry for Social Affairs, Health, Care and Consumer Protection Coronavirus information - Austria | Website |
| Austria | Public Health Agency of Austria COVID update page | Website |
| Belgium | Belgian Federal Government Coronavirus: reinforced measures | Website |
| Bulgaria | Ministry of Health Information (Bulgarian only) for citizens and medical professionals | Website |
| Croatia | Croatian Institute of Public Health Coronavirus information | Website |
| Croatia | Government of the Republic of Croatia COVID-19 Epidemic update | Website |
| Czech Republic | Ministry of Health Current incidence of COVID-19 in the Czech Republic | Website |
| Czech Republic | Office of the Government Coronavirus updates | Website |
| Denmark | Danish Health Authority Help and information - Questions and Answers on the Corona Virus COVID-19 | Website |
| Denmark | Transplantation Journal March Update
The first confirmed case of COVID-19 in Denmark was on February 27 from a skiing holiday in Northern Italy, since when it has grown to 1724 on March 25, with 350 in hospital and 87 in Intensive care and 34 have died. Initially most patients were believed to have been infected abroad, the majority are now acquiring the disease in Denmark. To prevent rapid spread there are border closures, closing of schools, universities and non-essential public work functions, a ban on any public or private event involving more than 10 people, closure of restaurants, bars, cafes, shopping centres, hair salons and similar businesses, and an extensive set of guidelines for the public to avoid spreading of the disease. | |
| England | London - Transplantation Journal March Update
The Liver Transplant program normally undertakes 250 liver transplants per year and currently has 150 patients on the waiting list. The events are changing rapidly, by day. Currently there are 60 COVID-19 positive patients in general Intensive Care, 35 ventilated. The general theatres have been converted to Intensive Care beds with the view of increasing number of infected patient requiring ITU management. Specialized theatres, Hepatobiliary, Cardiothoracic, Orthopaedic and Neurosurgical theatres are covering general surgery emergencies. With increasing numbers of staff testing positive or in self-isolation many transplant medical personal will be helping in Intensive Care and all Clinical Academics have been asked to stop research activity and return to full-time clinical work. Surgeons will also be trained in Intensive Care management. | |
| Finland | Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare Coronavirus Information Page | Website |
| France | Agence de Ia biomedecine Mise a jour des recommandations concernant I'utilisation d'organes et de tissus preleves chez des donneurs a risque d'infection par Ie virus SARS-CoV-2- STADE 3 de I'epidemie | |
| France | Gouvernement français Coronavirus information - France | Website |
| France | Management of SARS-CoV-2 infection in adult solid organ transplant patients (In French) April 2 - 14 page PDF Document produced by the Société Francophone de Transplantation (SFT), Société Francophone de Néphrologie, Dialyse et Transplantation (SFNDT) and Groupe Infection et Immunodépression, Société de pathologie infectieuse de langue française (SPILF). | |
| France | Ministry of Health "in French" | Website |
| France | Paris - Kidney - Transplantation Journal March Update To prevent transplant patients coming to the transplant center, clinics are undertaken through the phone and we have created a file of all 2300 follow up patients in order to send them information and new follow-up processes. The role of doctors has been modified to allow each of us to take care of a specific phase of care. Kidney transplantation with deceased and living donors has stopped until further notice. When transplant patients suspected of infection come to the hospital, they are seen the infectious disease unit, tested by PCR and then allocated to a COVID-19 positive hospital since ours has been designated COVID negative. In less than a week, 11 patients are positive, 10 tests are awaited, three patients are in Intensive Care and two are in a very bad situation. With COVID-19 positive patients we stop MMF and mTOR-inhibitors. In patients with ARDS, we also stop tacrolimus so patients remain only on steroids. We call each positive patient every day to monitor progress. The important clinical symptoms include anosmia and ageusia. CT scanning is critical to evaluate severity and oximetry to regulate O2 therapy. | |
| France | Paris - Liver - Transplantation Journal March Update
The burden of COVID-19 infection in France is lower than in Italy but, as of March 24th, almost 20,000 infected patients have been identified and 860 died including 5 doctors. The number of infected patients is growing exponentially but there are disparities between different regions in the country with a higher prevalence in the East of France and a lower prevalence in the West. The government has declared lockdown in the whole country. | |
| France | Strasbourg - Transplantation Journal March Update
All acute living and deceased donor kidney transplantation activity has totally stopped from 9th of March 2020 and most of the out patients are contacted and managed through video or tele conference. A Crisis Coordination Committee involving the manager of each medical unit helps manage the hospital on a day to day basis with a daily video conference. Patients are being separated into COVID-19 positive and negative groups when hospitalization is necessary. Medical staff are also separated, into dual on call teams on the nephrology ward, one for positive patients and one for negative. | |
| Germany | Ministry of Health COVID-19 Update page | Website |
| Germany | Regensburg - Transplantation Journal - April 7 2020 Update
Germany, Regensburg update 7th April 2020 | |
| Germany | Transplantation Journal March Update
Throughout Germany, living kidney donor transplant procedures are mostly being postponed. Cadaveric transplantation activities are being performed as normal for the time being. Testing for COVID-19 will be performed on cadaveric donors, but the results will generally not be used to determine if the organ is transplanted; the testing is for the purpose of recording whether the donor was positive or negative for the virus. | |
| Greece | National Organization of Public Health Coronavirus information - Greece | Website |
| Hungary | Government of Hungary Coronavirus information | Website |
| Ireland | Government of Ireland On this page you can view the latest information on how Ireland is responding to cases of COVID-19. | Website |
| Italy | Minestero della salud Aggiornamento delle misure di prevenzione della trasmissione dell'infezione da nuovo Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in Italia attraverso il trapianto di organi, tessuti e cellule. | |
| Italy | Ministero della Salute Coronavirus information - Italy | Website |
| Moldova | Ministry of Health, Labour and Social Protection Coronavirus information | Website |
| Netherlands | National Institute for Public Health and the Environment Official information on COViD-19 in the Netherlands | Website |
| Netherlands | Transplantation Journal March Update
The kidney transplant program of the largest transplant center stopped on March 13, 2020. Since then neither deceased donor nor living donor kidney transplantations have been performed. All living donor transplants have been put on hold, including patients scheduled to undergo blood group ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation already treated with alemtuzumab before the decision to stop acute kidney transplants. The main reason for stopping at present is the perception that immunosuppressed patients may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19. The six other Dutch transplant centers have all ceased their living donor kidney transplant activities while the centers that at present (March 23) face a smaller influx of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients will still transplant deceased donor kidneys. | |
| Netherlands | Transplantation policy in the Netherlands | Website |
| Norway | Health Norway Coronavirus information - Norway | Website |
| Poland | April 19 Update on COVID-19 This update was prepared in cooperation with Prof. Maciej Kosieradzki (President of Polish Union of Transplant Medicine) and Prof. Jarosław Czerwiński (Medical Director of Polish Transplant Coordinating Center Poltransplant.
In Poland we still have increasing number of patients with COVID-19 and currently (19th of April 2020) according to official data we have 9082 cases, 350 deaths and 1040 cured patients. Numerous social restrictions are applied – “stay at home” rule, wearing face mask in public places, keeping distance, restricted number of customers in shops and churches, closed schools and universities, most of business activities are limited, no sport and cultural events allowed. Hospitals are generally admitting urgent cases (most elective procedures except cancer cases are postponed). COVID-19 patients are treated in dedicated, infectious hospitals. | |
| Poland | Government of Poland The latest information about coronavirus | Website |
| Portugal | Directorate-General of Health Help and information - Coronavirus (COVID-19) | Website |
| Portugal | Ministério da Saúde Coronavirus information | Website |
| Romania | Department for Emergency Situation Coronavirus information - Romania | Website |
| Romania | Ministerul Afacerilor Interne Help and information - Coronavirus updates | Website |
| Russia | Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Information about the new coronavirus infection | Website |
| Russia | Russian Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing (Rospotrebnadzor) Coronavirus infection prevention | Website |
| Serbia | Ministry of Health Coronavirus information | Website |
| Serbia | Ministry of Health Coronavirus updates - Serbia | Website |
| Slovakia | Public Health Authority COVID update page | Website |
| Slovenia | Slovenija-transplant Institute for transplantation of organs and tissues of the Republic of Slovenia | Website |
| Spain | COVID-19 IN SPAIN AND ITS IMPACT UPON DONATION AND TRANSPLANTATION Beatriz Domínguez-Gil, Elisabeth Coll, Organización Nacional de Trasplantes, Madrid, Spain Transplantation Journal Update
Spain has been one of the most affected countries by the COVID-19 outbreak. As of 5 April 2020, the number of confirmed cases is 135,032, including 40,437 patients recovered, 6,931 having required admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), and 13,055 deaths, with a global mortality of 9.7%.1 The country is considered at epidemiological scenarios 3 (sustained community transmission) and 4 (intensive care capacity saturated and health-care system overwhelmed), as described by the European Centre for Disease Control and Prevention.2 | |
| Spain | Ministry of Health Help and information - Coronavirus information - Spain | Website |
| Spain | Organización Nacional de Trasplantes (ONT) April 13 Update - Spanish recommendations on organ donation and transplantation (ENG) | |
| Spain | Transplantation Journal March Update
When we learned about COVID-19 in China, it seemed like something happening far away that would never reach our homes. Then, we saw it happening in Italy, but still couldn’t understand the threat that the disease would become for our country. Isolation measures were decided by the government on March 12th, but it was clearly too late and the pandemic is hitting our cities to a point that medical care could collapse soon if heroic movements are not made. It is sad to see that other countries are making the same mistakes, waiting for the infection to explode before deciding drastic isolation measures that on the other side could jeopardize their economy. The infection spreads really fast: in less than two weeks our hospital has changed from not having a single case, to needing 50 intensive care beds and we are planning to open still more. | |
| Sweden | Public Health Agency of Sweden COVID-19 Update page | Website |
| Sweden | Swedish Civil Contingencies Agency Official information on the novel corona virus | Website |
| Switzerland | Federal Office of Public Health Coronavirus information - Switzerland | Website |
| Switzerland | SwissTransplant Fact sheet concerning donors | |
| Switzerland | Transplantation Journal March Update
In Switzerland, Ticino, which is close to Lombardy, was the first to be hard hit by COVID described graphically: “We recorded our first local case on the 1 March, in the first week the new cases were coming in slowly, now the gates have opened up and it is like the monsoon season in the rain forest.”. It is now apparent that the hardest hit cantons in Switzerland are Geneva and Vaud. The first national case was diagnosed on Feb 25. Today there are 7,726 confirmed cases with 99 fatalities, roughly 50% being in the 3 cantons of Geneva, Vaud and Ticino, but the wave will undoubtedly move in the north-east direction… | |
| Ukraine | Ministry of health of Ukraine Coronavirus information - Ukraine | Website |
| United Kingdom | NHS Coronavirus condition overview - United Kingdom | Website |
| United Kingdom | NHS Blood and Transplant COVID 19 Advice for Specialist Nurses Organ Donation and Specialist Requestors | |
| United Kingdom | NHS Blood and Transplant COVID-19: Clinical Advice | Website |
| United Kingdom | UK Government Coronavirus (COVID-19): what you need to do | Website |
| United Kingdom | UK NHS Advice for Clinicians | Website |
| United Kingdom | University of Liverpool -- COVID-19 Drug Interaction Prescribing Resources: The Liverpool Drug Interaction Group (based at the University of Liverpool, UK), in collaboration with the University Hospital of Basel (Switzerland) and Radboud UMC (Netherlands), have produced various materials in PDF format to aid the use of experimental agents in the treatment of COVID-19. | Website |
| Argentina | Ministry of Health Information, recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Nation and prevention measures (in spanish) | Website |
| Argentina | SADI/INCUCAI/SAT Commission on Infections in Solid Organ Transplantation In Spanish | |
| Brazil | Ministry of Health Coronavirus information - Brazil | Website |
| Brazil | Transplantation Journal April 6 Update
| |
| Chile | Ministry of Health Nuevo Coronavirus COVID-19 (Chile) | Website |
| Colombia | Ministry of Health COVID Information page | Website |
| Costa Rica | Costa Rica Ministry of Health Coronavirus information | Website |
| Cuba | Ministerio de Salud Pública en Cuba COVID update page | Website |
| Ecuador | Ministry of Public Health Coronavirus information | Website |
| Guatemala | Ministry of Public Health COVID update page | Website |
| Guyana | Ministry of Public Health COVID update page | Website |
| Honduras | Secretaría de Salud COVID update page | Website |
| Mexico | Government of Mexico - Health Secretary Coronavirus - Mexico | Website |
| Nicaragua | Ministerio de Salud COVID update page | Website |
| Panama | Ministry of Health Coronavirus information | Website |
| Paraguay | Ministry of Health COVID Page | Website |
| Peru | Ministry of Health information on preventing COVID-19 transmission | Website |
| Suriname | National Crisis Portal COVID update (in Dutch) | Website |
| Uruguay | Ministry of Public Health COVID update page | Website |
| Iran | Health Department COVID19 (Farsi) | Website |
| Iran | Transplantation Journal April 6 Update Submitted by Amir Kasraianfard, Mohssen Nassiri-Toosi, Ali Jafarian
Given the rapidly spreading coronavirus infection (COVID-19), there are several concerns and debates about performing organ transplantation. Risk of donor-derived disease transmission through organ transplantation is not clear at this time. 1 However, there are definite risks for nosocomial transmission to the live donors and recipients along with healthcare workers as well as significant risks for life-threatening infection and infectivity in immunocompromised transplant recipients. 2 Iran is one of the COVID-19 epicenters with 41495 registered cases and 2757 related deaths as of March 30, 2020 3 More than 3000 organ transplantations are performed annually nationwide, so it was mandatory to provide a new uniform standard transplantation protocol for donors and recipients in regard to COVID-19 risks, exposure and isolation and organizational leadership for priority setting in this rapidly emerging situation. 4,5 | |
| Israel | Ministry of Health Official information of the Israeli Ministry of Health on the coronavirus | Website |
| Israel | The Government of Israel Israel's emergency web portal on covid-19 | Website |
| Jordan | Ministry of Health COVID19 (Arabic) | Website |
| Kuwait | Ministry of Health COVID-19 Update Website | Website |
| Kuwait | Update on COVID-19 Kuwait is a small country with a population of 4 million. The present situation as of today is as follows:
As of 6th April, there are 665 diagnosed cases of Covid-19 in Kuwait with a population of 4 million inhabitants. There are 561 admitted for treatment, 20 of whom are critical and one death. 103 recovered from the virus and 2474 are under ministry quarantine.
Kuwait is a small country with a population of 4 million.
1. 2 new confirmed cases over last 24 hours. (The numbers ranged fro 1-17 cases daily) | |
| Lebanon | April 7 Update In Lebanon the first positive tested case was imported from Iran who was asymptomatic. She has recovered and at home Currently we have 540 cases with 18 death (the high number of death is alarming). We remained at one case for few days then we had another person who was on the same flight from Iran. 4 case were imported from Egypt 5 cases from UK and then 9 cases from Italy. The cases from Italy were the worst as they were priest who because of the Easter fast visited many families to offer the blessing for Easter which caused the spread of many cases. We have a group who attended a weeding in France and they came back with the infection. One of the cases from UK is a celebrity and upon arrival had a big birthday party for her daughter and again helped in the spread. We have a stay at home policy since the 19th of March and now we can only drive according to license plate numbers and o traffic on Sunday the stay at home is extended till 12th of April. For sample collection we have drive through for the outpatient. Many Lebanese who were outside are coming back and being tested upon arrival (430 came back on Sunday) we expect up to 12000 to come back. Most of the travelers are coming back from African countries but few are from EU. We test using PCR at designated centers by the MOH. Transmedical For Life being the reference Lab set the cost of the test for the public at 125000.00 Lebanese bounds equivalent to 80 US. But others are charging up to 300 US. The MOH has not yet allowed rapid testing. Our team is available at the airport to help testing upon arrival. There is a big shortage globally for PCR extraction kits which will soon cause problems for us. As for the accuracy of the tests we have been doing a study at our center in Canada and even with the PCR we have an error among manufacturers that is nearly 5% on average. Thus testing at different intervals may be advisable. | Read More |
| Oman | Ministry of Health COVID19 (Arabic) | Website |
| Qatar | Qatar ministry of health COVID-19 page | Website |
| Saudi Arabia | Saudi Ministry of Health COVID19 (Arabic) | Website |
| Saudi Arabia | Transplantation and COVID-19 Update The kingdom of Saudi Arabia, constituting the majority of the Arabian Peninsula with a total land area of 2.15 million km2 which is geographically considered as the largest sovereign state in the Western Asia. The Kingdom consists 34 million population which are composed of 62% citizens and 38% residents. The Kingdom have an active living and deceased donation and transplantation program including kidney (18 centers), liver (4), heart (2), lung (1), pancreas (2), small bowel (1), and tissue banking (2: cornea and bone). | |
| Syria | Update on COVID-19
The present Covid-19 situation in Syria as of April 7, 2020
1-The course of the disease in Syria: | |
| Turkey | Ankara - Transplantation Journal April Update Turkey update 04 April 2020 Submitted by Mehmet Haberal, Baskent University, Ankara
As of 04.04.2020, the number of confirmed cases in Turkey is 20921 with 425 deaths. A total of 484 people have fully recovered following treatment. Most of the victims in Turkey have been elderly. Turkey update March 2020 Submitted by Mehmet Haberal, Baskent University, Ankara
As of today, the number of confirmed cases is 1872 with 44 deaths. Most of the deaths in Turkey to date have been elderly, two were age 50-60, one was 91, and all the others were older than 61. Schools, universities, mosques, shopping malls and hairdressers have been temporarily closed and professional sports have been halted as part of measures to contain the virus. The Ministry of Health also announced that cafes, restaurants, pastry shops, and similar workplaces are closed and will only fulfill online orders and takeaway. There are restrictions on supermarkets, banks and public transport systems are obliged to limit their numbers to a maximum of 50% of their licensed capacity. Turkish citizens who are older than 65 and/or suffer from chronic illnesses are restricted from leaving home or even walking in open areas such as parks and gardens. | |
| Turkey | Government of Turkey COVID-19 Update page | Website |
| Turkey | Update on COVID-19 March 19 - Regarding Turkey, the number of confirmed cases are 1236 with 30 deaths.
First batch of rapid COVID-19 tests had already arrived and all private and foundation hospitals have been announced as pandemic hospitals as of last Friday. Transplant surgeries and other surgeries except cancer and urgent ones are postponed and this applies to all public and private hospitals in Turkey as well as Baskent University hospitals. | |
| UAE | Abu Dhabi Department of Health updates on COVID-19 | Website |
| UAE | Dubai Health Authority updates on COVID-19 | Website |
| UAE | UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention updates on COVID-19 | Website |
| Canada | Canadian Blood Services COVID-19 information | Website |
| Canada | Canadian Blood Services COVID-19: Update on organ donation and transplantation services | Website |
| Canada | Canadian Society of Transplantation COVID-19: Update | Website |
| Canada | Government of Canada COVID-19 updates, prevention and risks, symptoms and treatment, travel advice and financial response | Website |
| Canada | Government of Canada Canada COVID-19 Situational Awareness Dashboard | Website |
| Canada | Health Canada Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) information page | Website |
| Canada | Montreal - Transplantation Journal March Update
We have stopped Living Donor Kidney Transplantation and are not accepting offers of Deceased Donor Kidneys for recipients >70 years unless they are highly sensitized. All Deceased Donor kidney offers have been assessed on a case-by-case basis to assess individual risk/benefits for a transplant at this time, but we have now put a hold on transplants. We are planning to reassess that decision in two weeks. All donors must be tested for COVID-19 PCR before transplantation. All recipients have been screened by phone by the transplant nephrologist on-call about travel history, fever and respiratory symptoms, but we have not tested the recipients for COVID-19 PCR. | |
| Canada | Public Health Agency of Canada Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Outbreak update | Website |
| Canada | Toronto - Transplantation Journal March Update
Since March 16th, 2020, the two adult kidney transplant programs in Toronto, Canada, have suspended living donor kidney transplants and all new or ongoing workups in order to reduce the risk of COVID-19 exposure among recipient and donor candidates. Similarly, deceased donor kidney transplants and workups have been placed on pause except for patients currently active on the waiting list who have been deemed medically urgent (e.g., terminal vascular access) or those with cPRA > 99% whose access to kidneys are already very limited. The pancreas transplant program has followed a similar strategy to kidney. | |
| Canada | Vaccines and treatments for COVID-19: List of all COVID 19 clinical trials authorized by Health Canada Currently, the treatment of COVID-19 includes supportive care and treatment of any secondary infections, such as pneumonia. There are no drugs or vaccines approved, but there are now 20 clinical trials authorized in Canada with diagnostic equipment, supportive care and/or treatments for COVID-19. | Website |
| United States | American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases
Clinical Insights For Hepatology And Liver Transplant Providers During The COVID-19 Pandemic | |
| United States | American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB) The AATB Physicians Council Issues Donor Screening and Deferral Recommendations to Tissue Bank Medical Directors Related to the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Outbreak | |
| United States | American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB) Covid-19 Update | |
| United States | American Medical Association COVID-19 (2019 novel coronavirus) resource center for physicians | |
| United States | American Medical Association. COVID-19 (2019 novel coronavirus) resource center for physicians | Website |
| United States | American Society of Transplant Surgeons COVID-19 Strike Force - Guidance for Organ Retrieval | Website |
| United States | American Society of Transplantation (AST) Covid-19 Resources for the Transplant Community | |
| United States | American Society of Transplantation (AST) The AST's Infectious Disease Community of Practice has received queries from transplant and donation colleagues regarding the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). The following FAQs were developed with input of members from both the organ donation and transplantation communities to relay information on the current state of knowledge. | |
| United States | AST COVID-19 Resources for Transplant Community | Website |
| United States | Baltimore - Transplantation Journal April 4, Update Submitted by Daniel Brennan, ohns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore
There are now over 815 patients who are positive for COVID in the Johns Hopkins’s system and over 400 patients are considered Persons Under Investigation (PUI). Of these patients 342 are at home but with over 150 patients admitted in hospital and 68, are at Johns Hopkins Hospital. 30 are on ventilators and one is on ECMO. | |
| United States | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Interim Additional Guidance for Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations for Patients with Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19 in Outpatient Hemodialysis Facilities | Website |
| United States | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC and dialysis units | Website |
| United States | COVID-19 FAQs For Children with Solid Organ Transplant or Heart failure The Starzl Network for Excellence in Pediatric Transplantation and the Advanced Cardiac Therapies Improving Outcomes Network (ACTION) has developed an FAQ for pediatric transplant patients and their families. | |
| United States | East Coast - Transplantation Journal March Update
COVID-19 came recently to Baltimore and is increasing at rates similar to China and Europe despite early adaption of social distancing and closing restaurants and bars one week ago and now all non-essential businesses. As of Sunday (two days ago) there were 15 patients with COVID-19 admitted to Johns Hopkins. 9 of them are on ventilators. Two patients have been transplant patients. Both have been liver transplant patients. | |
| United States | Eye Bank Association of America (EBAA) CoronavirusDisease 2019(COVID-19) and Eye Tissue Donation | |
| United States | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Important Information for Human Cell, Tissue, or Cellular or Tissue-based Product (HCT/P) Establishments Regarding the 2019 Nove | |
| United States | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Important Information for Blood Establishments Regarding the NovelCoronavirus Outbreak | |
| United States | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Safety Alert on use of Fecal Microbiota for Transplantation and additional safety protections on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID19 | |
| United States | Mid-West - Transplantation Journal March Update
Covid-19 arrived here later than other areas of the US, but preparations are underway for an expected exponential increase. The goal for our response is to reduce risks to transplant candidates, donors, recipients, providers and also to prepare for the expected high influx of patients with suspected and confirmed COVID-19. All elective surgical procedures are on hold. Routine, non-urgent clinic visits are on hold or transitioned to telehealth. | |
| United States | New York - Transplantation Journal March Update
| |
| United States | Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) Information for transplant programs and OPOs regarding 2019 Novel Coronavirus | |
| United States | Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) OPTN updates on candidate data during 2020 COVID-19 emergency. March 17th 2020 | |
| United States | South - Transplantation Journal March Update
In the south we are just starting to see the volume of COVID-19 cases in our hospital spike this week and have instituted a number of steps. We have ceased kidney transplant evaluations and limited liver transplant evaluations to those with high MELD scores. Post-transplant follow up appointments are being conducted via telemedicine to the maximum extent possible. Scheduled living donor kidney transplants are being postponed. Deceased donor kidney transplant activity continues at a lower level with emphasis on selection of donors not expected to have DGF to minimize the post-transplant hospital stay. Deceased donor liver transplantation continues with all transplant candidates screened for COVI-19 risk prior to being called in. | |
| United States | UNOS Member information regarding COVID-19 News and updates for organ procurement organizations and transplant programs | Website |
| United States | West Coast - Transplantation Journal March Update
The region started “shelter in place” on 16th March with the rest of the state following 5 days later. While there have been clusters of COVID-19 in Santa Clara and Los Angeles, San Francisco has seen relatively few cases. In UCSF there are currently three patients in Intensive Care and 8 others hospitalized. About 30 ae awaiting test results. |
| Australia | Australian Government Coronavirus information - Australia | Website |
| Australia | Department of Health Help and information Coronavirus (COVID-19) health alert | Website |
| Australia | Department of health Latest news | Website |
| Australia | Transplantation Journal March Update
Acute Transplantation activity has substantively reduced nationally. Living donor kidney transplantation has stopped for the past few days and deceased donor transplantation which was being assessed on a case by case basis has also stopped entirely for a period, depending on hospital Intensive Care and Emergency Department capacity. All deceased donors have required COVID-testing but the number of deceased donors has dropped dramatically. We have also slowed down all elective surgery, endoscopies and bronchoscopies, as well as auxiliary and allied health services. The government has today banned all non-urgent elective surgery. | |
| New Zealand | The New Zealand Government Updates on COVID-19 | |
| New Zealand | Transplantation Journal March Update
As at 25 March 2020, there is limited community transmission of COVID-19 in New Zealand, with most cases related to overseas travel, or close contacts of people who have recently returned from overseas. NZ is currently going into ‘lockdown’, which will see all people isolating at home and only essential businesses including healthcare and food production continuing. |
Publications
Mortality rates in Transplant recipients infected with SARSCov2 and diagnosed as having COVID-19. April 2020
There has been a global assumption that transplant recipients would be particularly endangered by the current pandemic of Coronovirus. Data have however been quite sparse and the ability to create a global picture has been limited.
Case reports are now giving way to small case series in the literature. The Transplantation Journal has collected the following data from correspondents from around the world and offers it as a very limited and highly flawed view of what might be happening.
Data from New York centres has been supplied from New York and are presented separately as they provide the most comprehensive view of the increased risk of death for transplant recipients across the spectrum of organ transplant types. The story of a widespread tragedy in the field of Transplantation is not underestimating the current data. Careful inspection of the data could be seen to show two features:
- High mortality rates in the range of 15-30% for transplant recipients in the countries and regions with high incidences and high mortality rates in the general populations.
- Low incidence and no mortality for transplant recipients in low incidence countries, suggesting that transplant recipients may have heeded well the messages to isolate themselves from the virus.
Country |
COVID pos |
alive In ICU |
Dead |
Mongolia |
0 |
0 |
0 |
New Zealand |
0 |
0 |
0 |
India (5 States) |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Denmark |
2 |
0 |
1 |
Singapore |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Hong Kong |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Brazil |
27 |
3 |
7 |
Korea |
2 |
0 |
0 |
Australia |
3 |
0 |
0 |
USA |
9 |
1 |
0 |
Italy |
20 |
4 |
5 |
Strasbourg |
48 |
10 |
9 |
London |
7 |
4 |
1 |
Totals |
120 |
22 |
23 |
(All data reports above are at the time of reporting in April)


This report was published in Transplantation:
April 1, 2020 - Volume Online First - Issue -
doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003258
The COVID 19 pandemic has hit the entire world in an almost unprecedented way. The crisis has spread rapidly, disease burden and casualties continue to rise, and the impact of the crisis is spreading through developing countries. Social distancing, travel restrictions, and intensified testing have improved the rate of rise in new cases in some regions, however, it remains unclear when normality will return. Mechanisms of the disease remain largely unclear; treatment, if available, is mostly supportive. As during times of war, the challenges of the Coronavirus crisis change our views in almost any aspect.The Science journals are striving to provide the best and most timely research, analysis, and news coverage of COVID-19 and the coronavirus that causes it. All content is free to access. Science's COVID-19 reporting is supported by the Pulitzer Center.
View Coronona Virus Dedicated page
Highlighted Articles:
April 25 - Letter to the Editor - Covid-19 and Kidney Transplantation
View Article
| Publication | American Journal of TransplantationHighlighted Articles:May 5 - PERSONAL VIEWPOINT - Utilization of deceased donors during a pandemic: An argument against using SARS‐CoV‐2 positive donors May 12 - PERSONAL VIEWPOINT - Use of SARS‐CoV‐2 infected deceased organ donors: Should we always “just say no?” | |
| Publication | New England Journal of Medicine A collection of articles and other resources on the Coronavirus (Covid-19) outbreak, including clinical reports, management guidelines, and commentary. View Coronona Virus Dedicated page Highlighted Articles:April 25 - Letter to the Editor - Covid-19 and Kidney Transplantation | Website |
| Publication | American Society for Clinical Investigation - COVID-19 article collection Highlighted Article: Kidney diseases in the time of COVID-19: major challenges to patient care | Website |
| Publication | Annals of Internal Medicine | Website |
| Publication | CA - A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | Website |
| Publication | European Heart Journal | Website |
| Publication | European Urology | Website |
| Publication | JAMA Internal Medicine | Website |
| Publication | Journal of Hepatology | Website |
| Publication | Nature Reviews Cancer | Website |
| Publication | Nature Reviews Genetics | Website |
| Publication | Physiological Reviews | Website |
| Publication | Science Translational Medicine | Website |
| Publication | The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Highlighted Article: COVID-19 in long-term liver transplant patients: preliminary experience from an Italian transplant centre in Lombardy | Website |
| Publication | Trends in Immunology | Website |
Latest Videos
| American Medical Association | April 20 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 17 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 16 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 15 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 14 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 13 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 10 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 9 - COVID-19: AMA’s National Physician Townhall The American Medical Association invites you to a live conversation with AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, MA, and a panel of AMA health care experts on challenges and concerns facing physicians during this unprecedented COVID-19 crisis. | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 8 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 7 - National Address from the American Medical Association President President | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 7 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 6 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 3 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 2 Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 2 - Prioritizing Equity: Experience of Physicians of Color &COVID-19 | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | April 1 - Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | March 31 - Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | March 30 - Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | March 27 - Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | March 26 - Update | Play Video |
| American Medical Association | March 25 - Update | Play Video |
Questions about testing, chloroquine toxicity, duration of immunity and reinfection, and what to expect next are gripping the US as the novel coronavirus spreads. Preeti Malani MD, Professor of Medicine and Chief Health Officer at the University of Michigan discusses recent developments in a live conversation with JAMA Editor Howard Bauchner. Originally streamed on April 6, 2020.
CME for watching this livestream will be available here: https://ja.ma/covidqa Coronavirus Resource page from the JAMA Network: https://ja.ma/covidyt
1:55 Overview of Dr Bauchner's interview with Dr Malani
2:01 Case-fatality rate
4:50 CDC’s changing views on masks - what should we make of the change?
7:45 Should or shouldn’t I wear a mask?
8:46 Medical workers
9:49 PCR tests, should we trust the accuracy?
11:29 Can you become reinfected?
13:18 Serology and the likelihood of antibody testing (who is immune/ has antibodies to the virus) and being able to go to work if proven immune.
16:01 How long can we assume we are immune for, given the data we have.
17:36 How is COVID-19 spreading? Droplets versus aerolization spread. Coughs and sneezes or just through the air?
21:00 How long does the coronavirus live on packages, newspapers, groceries?
23:50 Infected tiger at the Bronx Zoo. Animal responses to COVID
24:52 Discussion on study of viral load found in stool/ 14 day quarantine still to be trusted?
29:51 Health care workers
33:04 What will work for treatment of COVID. Hydroxychloroquine discussion. Remdesivir trials.
35:25 Social distancing, how long will it go on?
Contact
Address
The Transplantation Society
International Headquarters
740 Notre-Dame Ouest
Suite 1245
Montréal, QC, H3C 3X6
Canada
Используйте Вавада казино для игры с бонусом — активируйте промокод и начните выигрывать уже сегодня!